Page 493 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 493
Section 18.3 Forming and Shaping of Glass 473
an old-fashioned clothes wringer. The solidifying glass
Glass products generally can be categorized as follows:
I. Flat sheets or plates ranging in thickness from about 0.8 to 10 mm, such as
window glass, glass doors, and tabletops.
2. Rods and tubing used for chemicals, neon lights, and decorative artifacts.
3. Discrete products such as bottles, vases, headlights, and television tubes.
4. Glass fibers to reinforce composite materials (Section 9.2.1) and for use in
fiber optics.
All glass forming and shaping processes begin with molten glass, typically in
the range from 1000° to 1200°C. The glass has the appearance of a red-hot, viscous
syrup and is supplied from a melting furnace or tank.
l8.3.l Flat-sheet and Plate Glass
Flat-sheet glass can be made by the float glass method or by drawing or rolling it
from the molten state (all three methods are continuous processes):
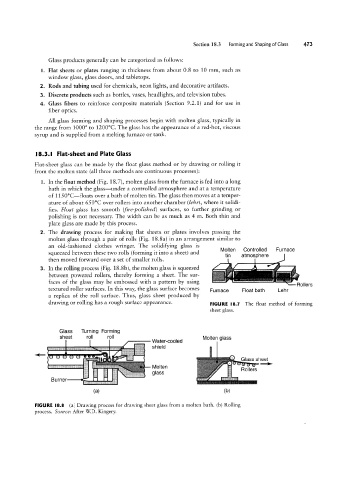
l. In the float method (Fig. 18.7), molten glass from the furnace is fed into a long
bath in which the glass-under a controlled atmosphere and at a temperature
of 115O°C-floats over a bath of molten tin. The glass then moves at a temper-
ature of about 65 0°C over rollers into another chamber (le/ar), where it solidi-
fies. Float glass has smooth (/Qre-polished) surfaces, so further grinding or
polishing is not necessary. The width can be as much as 4 m. Both thin and
between powered rollers, thereby forming a sheet. The sur- Controlled Furnace
plate glass are made by this process.
2. The drawing process for making flat sheets or plates involves passing the
molten glass through a pair of rolls (Fig. 18.8a) in an arrangement similar to
is
Molten
squeezed between these two rolls (forming it into a sheet) and
gg
h
1'
atmosp ere
then moved forward over a set of smaller rolls.
3. In the rolling process (Fig. 18.8b), the molten glass is squeezed In ~°*‘~‘~~~~~~~'~~~'~»~~~~~‘~~~'»»»»»»»»r--»»»-»»»»
,
faces of the glass may be embossed with a pattern by using * °"rr”°'° 539' Rollers
textured roller surfaces. In this way, the glass surface becomes Furnace Float bath Lehr
a replica of the roll surface. Thus, glass sheet produced by
drawing or rolling has a rough surface appearance. FIGURE |8.1 The float method of forming
sheet glass.
Water-cooled M O en gass
Turning Forming
Glass
sheet
roll
roll
|t
if § “"°"e" Rollers Sheet
(_ rrrrr § Shield
° ° ° ° ° *Wi
_
Bum-°
9'aSS
(H) (D)
FIGURE |8.8 (a) Drawing process for drawing sheet glass from a molten bath. (b) Rolling
process. Source: After WD. Kingery.