Page 34 - Marine Structural Design
P. 34
Chapter I Introduction 11
"T Load Strength
E
n
Magnitude
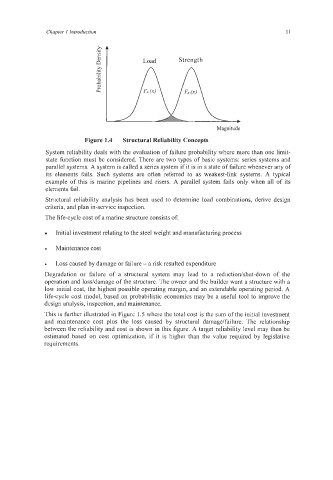
Figure 1.4 Structural Reliability Concepts
System reliability deals with the evaluation of failure probability where more than one limit-
state function must be considered. There are two types of basic systems: series systems and
parallel systems. A system is called a series system if it is in a state of failure whenever any of
its elements fails. Such systems are often referred to as weakest-link systems. A typical
example of this is marine pipelines and risers. A parallel system fails only when all of its
elements fail.
Structural reliability analysis has been used to determine load combinations, derive design
criteria, and plan in-service inspection.
The life-cycle cost of a marine structure consists of:
Initial investment relating to the steel weight and manufacturing process
. Maintenance cost
. Loss caused by damage or failure - a risk resulted expenditure
Degradation or failure of a structural system may lead to a reductiodshut-down of the
operation and losddamage of the structure. The owner and the builder want a structure with a
low initial cost, the highest possible operating margin, and an extendable operating period. A
life-cycle cost model, based on probabilistic economics may be a useful tool to improve the
design analysis, inspection, and maintenance.
This is further illustrated in Figure 1.5 where the total cost is the sum of the initial investment
and maintenance cost plus the loss caused by structural damage/failure. The relationship
between the reliability and cost is shown in this figure. A target reliability level may then be
estimated based on cost optimization, if it is higher than the value required by legislative
requirements.