Page 38 - Marine Structural Design
P. 38
Chapter I Introduction 15
I FunctT 1 iLoar 1 I Ultimate , strength, 1 Structural reliability, I
requirements
Fatigue and fi-ature Risk assessment
7- 7-
i3
Finish
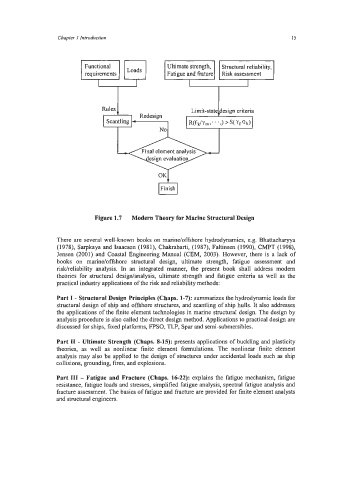
Figure 1.7 Modern Theory for Marine Structural Design
There are several well-known books on marindoffshore hydrodynamics, e.g. Bhattacharyya
(1978), Sarpkaya and Isaacson (1981), Chakrabarti, (1987), Faltinsen (1990), CMPT (1998),
Jensen (2001) and Coastal Engineering Manual (CEM, 2003). However, there is a lack of
books on marine/offshore structural design, ultimate strength, fatigue assessment and
riskheliability analysis. In an integrated manner, the present book shall address modem
theories for structural desigrdanalysis, ultimate strength and fatigue criteria as well as the
practical industry applications of the risk and reliability methods:
Part I - Structural Design Principles (Chaps. 1-7): summarizes the hydrodynamic loads for
structural design of ship and offshore structures, and scantling of ship hulls. It also addresses
the applications of the finite element technologies in marine structural design. The design by
analysis procedure is also called the direct design method. Applications to practical design are
discussed for ships, fixed platforms, FPSO, TLP, Spar and semi-submersibles.
Part I1 - Ultimate Strength (Chaps. 8-15): presents applications of buckling and plasticity
theories, as well as nonlinear finite element formulations. The nonlinear finite element
analysis may also be applied to the design of structures under accidental loads such as ship
collisions, grounding, fires, and explosions.
Part I11 - Fatigue and Fracture (Chaps. 16-22): explains the fatigue mechanism, fatigue
resistance, fatigue loads &d stresses, simplified fatigue analysis, spectral fatigue analysis and
fracture assessment. The basics of fatigue and fracture are provided for finite element analysts
and structural engineers.