Page 621 - Marine Structural Design
P. 621
Chapter 34 Risk Centered Maintenance 591
System: Performed by:
Ref. Drawing no: Date:
Failure Effects
Y
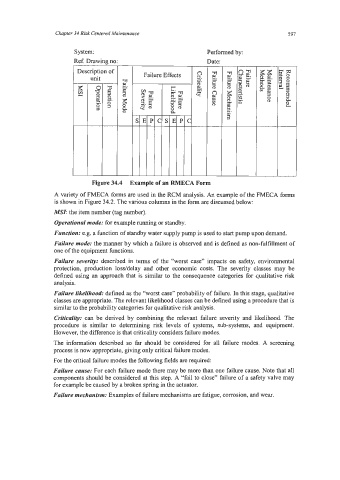
Figure 34.4 Example of an RMECA Form
A variety of FMECA forms are used in the RCM analysis. An example of the FMECA forms
is shown in Figure 34.2. The various columns in the form are discussed below:
MSI: the item number (tag number).
OperationaI mode: for example running or standby.
Function: e.g. a function of standby water supply pump is used to start pump upon demand.
Failure mode: the manner by which a failure is observed and is defined as non-hlfillment of
one of the equipment functions.
Failure severity: described in terms of the “worst case” impacts on safety, environmental
protection, production loss/delay and other economic costs. The severity classes may be
defined using an approach that is similar to the consequence categories for qualitative risk
analysis.
Failure likelihood: defined as the “worst case” probability of failure. In this stage, qualitative
classes are appropriate. The relevant likelihood classes can be defined using a procedure that is
similar to the probability categories for qualitative risk analysis.
CriticaIity: can be derived by combining the relevant failure severity and likelihood. The
procedure is similar to determining risk levels of systems, sub-systems, and equipment.
However, the difference is that criticality considers failure modes.
The information described so far should be considered for all failure modes. A screening
process is now appropriate, giving only critical failure modes.
For the critical failure modes the following fields are required:
Failure came: For each failure mode there may be more than one failure cause. Note that a11
components should be considered at this step. A “fail to close” failure of a safety valve may
for example be caused by a broken spring in the actuator.
Failure mechanism: Examples of failure mechanisms are fatigue, corrosion, and wear.