Page 617 - Marine Structural Design
P. 617
Chapter 34 Risk Centered Maintenance 593
Frequency Categories Nominal Range of Frequency per Year
A - Often > lo-’
B - Likely I lo-’ to lo-*
C - Unlikely io-2 to 10”
D - Incredible < lo4
CONSEQUENCE CATEGORY
*
$8
82
EU
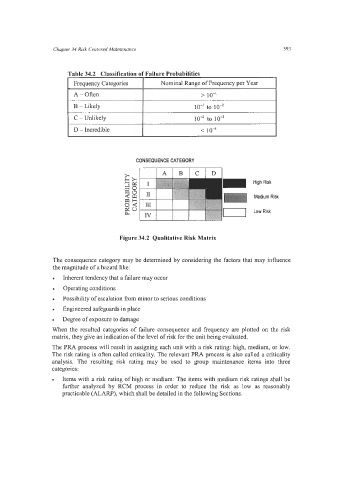
Figure 34.2 Qualitative Risk Matrix
The consequence category may be determined by considering the factors that may influence
the magnitude of a hazard like:
Inherent tendency that a failure may occur
Operating conditions
Possibility of escalation from minor to serious conditions
Engineered safeguards in place
Degree of exposure to damage
When the resulted categories of failure consequence and frequency are plotted on the risk
matrix, they give an indication of the level of risk for the unit being evaluated.
The PRA process will result in assigning each unit with a risk rating: high, medium, or low.
The risk rating is often called criticality. The relevant PRA process is also called a criticality
analysis. The resulting risk rating may be used to group maintenance items into three
categories:
Items with a risk rating of high or medium: The items with medium risk ratings shall be
further analyzed by RCM process in order to reduce the risk as low as reasonably
practicable (ALARF’), which shall be detailed in the following Sections.