Page 71 - Marine Structural Design
P. 71
Chapter 3 Loah and Dynamic Response for Ofshore Structures 47
Damping forces are important when a system is under resonant loading, which is cyclically
applied at one of the system's natural frequencies. They consist of hydrodynamic damping,
structural damping, soil/foundation damping etc.
The above is just a road map to floating structure dynamics because this book is devoted to
structural design. Details of motion and load calculations are available from Bhattacharyya
(1978), Beck et a1 (1989), Faltinsen (1990), and CMPT (1998).
Surge (m)
I I I I I
1 I I I I
-2
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Time (s)
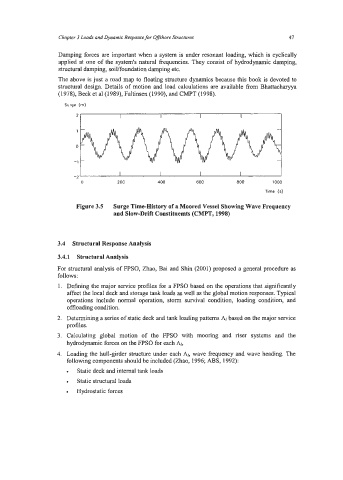
Figure 3.5 Surge Time-History of 8 Moored Vessel Showing Wave Frequency
and Slow-Drift Constituemts (CMPT, 1998)
3.4 Structural Response Analysis
3.4.1 Structural Analysis
For structural analysis of FPSO, Zhao, Bai and Shin (2001) proposed a general procedure as
follows:
1. Defining the major service profiles for a FPSO based on the operations that significantly
affect the local deck and storage tank loads as well as the global motion responses. Typical
operations include normal operation, storm survival condition, loading condition, and
offloading condition.
2. Determining a series of static deck and tank loading patterns AI based on the major service
profiles.
3. Calculating global motion of the FPSO with mooring and riser systems and the
hydrodynamic forces on the FPSO for each AI,
4. Loading the hull-girder structure under each AI, wave frequency and wave heading. The
following components should be included (Zhao, 1996; ABS, 1992):
Static deck and internal tank loads
Static structural loads
Hydrostatic forces