Page 145 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 145
4.5 Dislocations—Linear Defects • 117
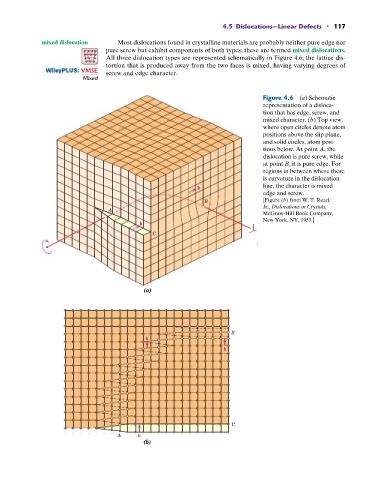
mixed dislocation Most dislocations found in crystalline materials are probably neither pure edge nor
pure screw but exhibit components of both types; these are termed mixed dislocations.
All three dislocation types are represented schematically in Figure 4.6; the lattice dis-
tortion that is produced away from the two faces is mixed, having varying degrees of
: VMSE screw and edge character.
Mixed
Figure 4.6 (a) Schematic
representation of a disloca-
tion that has edge, screw, and
mixed character. (b) Top view,
where open circles denote atom
positions above the slip plane,
and solid circles, atom posi-
tions below. At point A, the
dislocation is pure screw, while
at point B, it is pure edge. For
regions in between where there
is curvature in the dislocation
line, the character is mixed
b
edge and screw.
B [Figure (b) from W. T. Read,
Jr., Dislocations in Crystals,
A
McGraw-Hill Book Company,
New York, NY, 1953.]
b
C
(a)
B
b
b
C
A b
(b)