Page 148 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 148
120 • Chapter 4 / Imperfections in Solids
b
Twin plane (boundary)
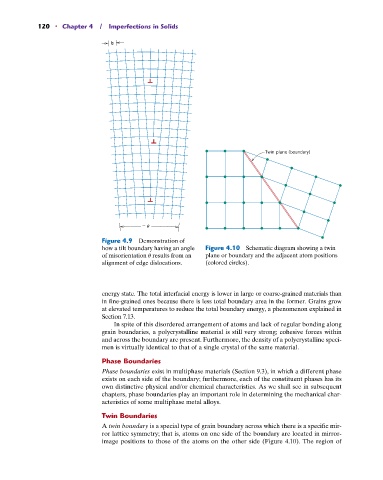
Figure 4.9 Demonstration of
how a tilt boundary having an angle Figure 4.10 Schematic diagram showing a twin
of misorientation u results from an plane or boundary and the adjacent atom positions
alignment of edge dislocations. (colored circles).
energy state. The total interfacial energy is lower in large or coarse-grained materials than
in fine-grained ones because there is less total boundary area in the former. Grains grow
at elevated temperatures to reduce the total boundary energy, a phenomenon explained in
Section 7.13.
In spite of this disordered arrangement of atoms and lack of regular bonding along
grain boundaries, a polycrystalline material is still very strong; cohesive forces within
and across the boundary are present. Furthermore, the density of a polycrystalline speci-
men is virtually identical to that of a single crystal of the same material.
Phase Boundaries
Phase boundaries exist in multiphase materials (Section 9.3), in which a different phase
exists on each side of the boundary; furthermore, each of the constituent phases has its
own distinctive physical and/or chemical characteristics. As we shall see in subsequent
chapters, phase boundaries play an important role in determining the mechanical char-
acteristics of some multiphase metal alloys.
Twin Boundaries
A twin boundary is a special type of grain boundary across which there is a specific mir-
ror lattice symmetry; that is, atoms on one side of the boundary are located in mirror-
image positions to those of the atoms on the other side (Figure 4.10). The region of