Page 158 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 158
130 • Chapter 4 / Imperfections in Solids
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 4.5
Grain-Size Computations Using ASTM and Intercept Methods
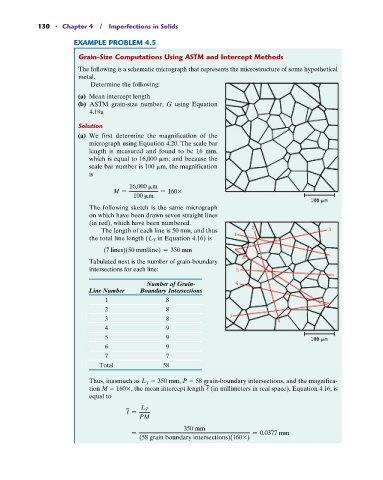
The following is a schematic micrograph that represents the microstructure of some hypothetical
metal.
Determine the following:
(a) Mean intercept length
(b) ASTM grain-size number, G using Equation
4.19a
Solution
(a) We first determine the magnification of the
micrograph using Equation 4.20. The scale bar
length is measured and found to be 16 mm,
which is equal to 16,000
m; and because the
scale bar number is 100
m, the magnification
is
16,000
m
M = = 160*
100
m
The following sketch is the same micrograph
on which have been drawn seven straight lines
(in red), which have been numbered.
The length of each line is 50 mm, and thus 2 3
the total line length (L T in Equation 4.16) is 1
(7 lines)(50 mm/line) = 350 mm
4
Tabulated next is the number of grain-boundary
intersections for each line: 5
Number of Grain- 6
Line Number Boundary Intersections
1 8
2 8
3 8 7
4 9
5 9
6 9
7 7
Total 58
Thus, inasmuch as L T 350 mm, P 58 grain-boundary intersections, and the magnifica-
tion M 160 , the mean intercept length / (in millimeters in real space), Equation 4.16, is
equal to
L T
/ =
PM
350 mm
= = 0.0377 mm
(58 grain boundary intersections)(160*)