Page 234 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 234
206 • Chapter 6 / Mechanical Properties of Metals
Symbol Meaning
TS Tensile strength
Strain values perpendicular to the direction of load application
(i.e., the transverse direction)
P x , P y
Strain value in the direction of load application (i.e., the longitudinal
direction)
P z
Yield strength
s y
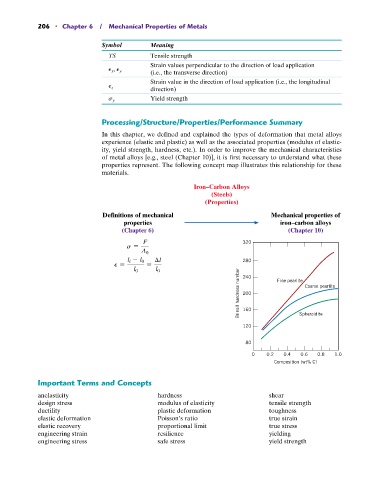
Processing/Structure/Properties/Performance Summary
In this chapter, we defined and explained the types of deformation that metal alloys
experience (elastic and plastic) as well as the associated properties (modulus of elastic-
ity, yield strength, hardness, etc.). In order to improve the mechanical characteristics
of metal alloys [e.g., steel (Chapter 10)], it is first necessary to understand what these
properties represent. The following concept map illustrates this relationship for these
materials.
Iron–Carbon Alloys
(Steels)
(Properties)
Definitions of mechanical Mechanical properties of
properties iron–carbon alloys
(Chapter 6) (Chapter 10)
F 320
s =
A 0
l i - l 0 l 280
P = =
Brinell hardness number 200 Coarse pearlite
l 0 l 0 240 Fine pearlite
160
120 Spheroidite
80
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Composition (wt% C)
Important Terms and Concepts
anelasticity hardness shear
design stress modulus of elasticity tensile strength
ductility plastic deformation toughness
elastic deformation Poisson’s ratio true strain
elastic recovery proportional limit true stress
engineering strain resilience yielding
engineering stress safe stress yield strength