Page 318 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 318
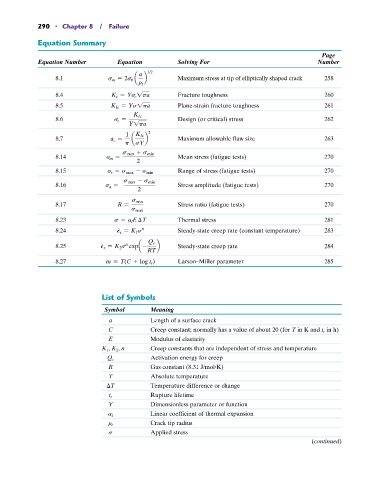
290 • Chapter 8 / Failure
Equation Summary
Page
Equation Number Equation Solving For Number
a 1/2
8.1 s m = 2s 0 a b Maximum stress at tip of elliptically shaped crack 258
r t
8.4 K c = Ys c 1pa Fracture toughness 260
8.5 K Ic = Ys1pa Plane-strain fracture toughness 261
8.6 s c = K Ic Design (or critical) stress 262
Y1pa
1 K Ic 2
8.7 a c = a b Maximum allowable flaw size 263
p sY
s max + s min
8.14 s m = Mean stress (fatigue tests) 270
2
8.15 s r = s max - s min Range of stress (fatigue tests) 270
s max - s min
8.16 s a = Stress amplitude (fatigue tests) 270
2
8.17 R = s min Stress ratio (fatigue tests) 270
s max
8.23 s = a l E T Thermal stress 281
#
8.24 P s = K 1 s Steady-state creep rate (constant temperature) 283
n
#
n
8.25 P s = K 2 s expa - Q c b Steady-state creep rate 284
RT
8.27 m = T(C + log t r ) Larson–Miller parameter 285
List of Symbols
Symbol Meaning
Length of a surface crack
a
C Creep constant; normally has a value of about 20 (for T in K and t r in h)
E Modulus of elasticity
K 1 , K 2 , n Creep constants that are independent of stress and temperature
Q c Activation energy for creep
#
R Gas constant (8.31 J/mol K)
T Absolute temperature
T Temperature difference or change
Rupture lifetime
t r
Y Dimensionless parameter or function
a l Linear coefficient of thermal expansion
r t Crack tip radius
s Applied stress
(continued)