Page 74 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 74
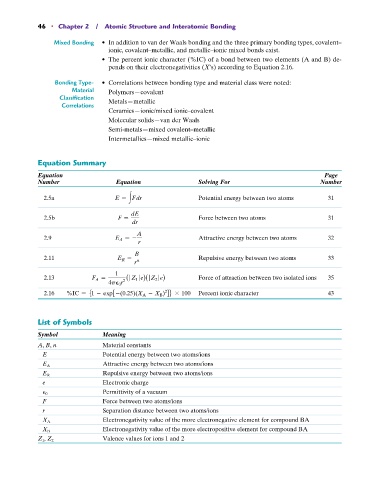
46 • Chapter 2 / Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding
Mixed Bonding • In addition to van der Waals bonding and the three primary bonding types, covalent–
ionic, covalent–metallic, and metallic–ionic mixed bonds exist.
• The percent ionic character (%IC) of a bond between two elements (A and B) de-
pends on their electronegativities (X’s) according to Equation 2.16.
Bonding Type- • Correlations between bonding type and material class were noted:
Material Polymers—covalent
Classification Metals—metallic
Correlations
Ceramics—ionic/mixed ionic–covalent
Molecular solids—van der Waals
Semi-metals—mixed covalent–metallic
Intermetallics—mixed metallic–ionic
Equation Summary
Equation Page
Number Equation Solving For Number
2.5a E = 3 F dr Potential energy between two atoms 31
dE
2.5b F = Force between two atoms 31
dr
A
2.9 E A = - Attractive energy between two atoms 32
r
B
2.11 E R = Repulsive energy between two atoms 33
r n
1
2.13 F A = ( Z 1 e)( Z 2 e) Force of attraction between two isolated ions 35
4pP 0 r 2
2
2.16 %IC = 51 - exp[ -(0.25)(X A - X B ) ]6 * 100 Percent ionic character 43
List of Symbols
Symbol Meaning
A, B, n Material constants
E Potential energy between two atoms/ions
E A Attractive energy between two atoms/ions
E R Repulsive energy between two atoms/ions
e Electronic charge
Permittivity of a vacuum
P 0
F Force between two atoms/ions
r Separation distance between two atoms/ions
X A Electronegativity value of the more electronegative element for compound BA
X B Electronegativity value of the more electropositive element for compound BA
Z 1 , Z 2 Valence values for ions 1 and 2