Page 108 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 108
APPLIED MECHANICS 97
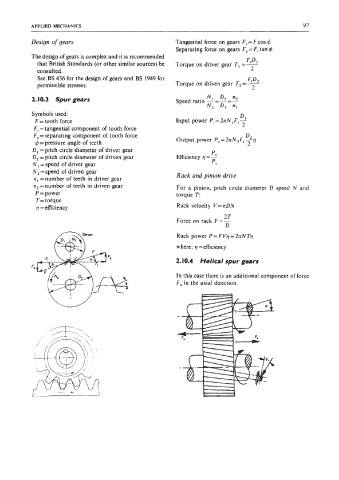
Design of gears Tangential force on gears F, = F cos r#J
Separating force on gears F, = F, tan q5
The design of gears is complex and it is recommended
FIDI
that British Standards (or other similar sources) be Torque on driver gear TI =-
consulted. 2
See BS 436 for the design of gears and BS 1949 for FID,
permissible stresses. Torque on driven gear T, =- 2
. N, D, n
2.10.3 Spur gears Speed ratio ---=A
N2 D, n,
Symbols used: D
F = tooth force Input power Pi = 271N , F, 2
F, = tangential component of tooth force
F, = separating component of tooth force D
r#J =pressure angle of teeth Output power P,=2nN2F,~q
2
D, =pitch circle diameter of driver gear
Po
D, =pitch circle diameter of driven gear Efficiency q = -
N, =speed of driver gear pi
N, =speed of driven gear Rack and pinion drive
n, =number of teeth in driver gear
n2 =number of teeth in driven gear For a pinion, pitch circle diameter D speed N and
P =power torque T:
T= torque
9 =efficiency Rack velocity V=nDN
2T
Force on rack F=-
D
Rack power P = F Vq = 2nN Tq
where: 9 =efficiency.
2.10.4 Helical spur gears
In this case there is an additional component of force
Fa in the axial direction.