Page 104 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 104
APPLIED MECHANICS 93
2.9.5 Rolling bearings (4) Because of extremely small clearance they permit
more accurate location; important for gears for
The term ‘rolling bearing’ refers to both ball and roller example.
bearings. Ball bearings of the journal type are used for (5) Self-aligning types permit angular deflection of the
transverse loads but will take a considerable axial shaft and misalignment.
load. They may also be used for thrust bearings.
Rollers are used for journal bearings but will not take Disadvantages of rolling bearings
axial load. Taper roller bearings will take axial thrust
as well as transverse load. (1) The outside diameter is large.
(2) The noise is greater than for plain bearings,
Advantages of rolling bearings especially at high speeds.
(3) There is greater need of cleanliness when fitted to
(1) Coefficient of friction is low compared with plain achieve correct life.
bearings especially at low speeds. This results in (4) They cannot always be fitted, e.g. on crankshafts.
lower power loss. (5) They are more expensive for small quantities but
(2) Wear is negligible if lubrication is correct. relatively cheap when produced in large quanti-
(3) They are much shorter than plain bearings and ties.
take up less axial space. (6) Failure may be catastrophic.
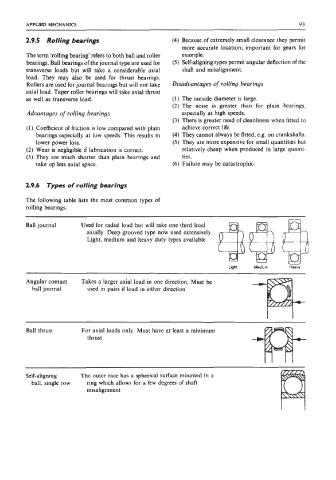
2.9.6 Types of rolling bearings
The following table lists the most common types of
rolling bearings.
Ball journal Used for radial load but will take one third load
axially. Deep grooved type now used extensively.
Light, medium and heavy duty types available.
Light Medium Heavy
Angular contact Takes a larger axial load in one direction. Must be
hall journal used in pairs if load in either direction
Self-aligning The outer race has a spherical surface mounted in a
ball, single row ring which allows for a few degrees of shaft
misalignment