Page 253 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 253
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 24 1
require protection by painting, plating, tinning, gal- 6.12.3 Stress corrosion cracking
vanizing, etc.
Under tensile stress and in a corrosive environment
some metals develop surface cracks called ‘stress
Copper and copper based alloys
corrosion cracking’ which is time dependent and may
take months to develop. It is avoided by minimizing
Copper An oxide coating prevents corrosion from stress and/or improving the environment.
water and atmosphere, e.g. water pipes.
Environments causing stress corrosion cracking
Brass ‘Yellow brass’ (> 15%Zn) is subject to ‘de-
zincification’ in hot water. ‘Red brass’ (85%Cu
minimum) is much better. Resistance is improved by Material Environment
the addition of arsenic or antimony. Steels Caustic solutions
Bronzes Over 5% tin gives better resistance than Stainless steels 50-60 “C Chloride solutions
brass, especially to sea water and stress corrosion Aluminium and alloys Chloride solutions
cracking. Aluminium bronze is good at elevated Copper alloys Ammonia atmosphere,
temperatures. Silicon bronze is as good but also has sometimes neutral
weldability; it is used for tanks. water
Acrylics Chlorinated solvents
Cupronickel This has the best resistance of all copper
alloys and is used for heat-exchanger tubes.
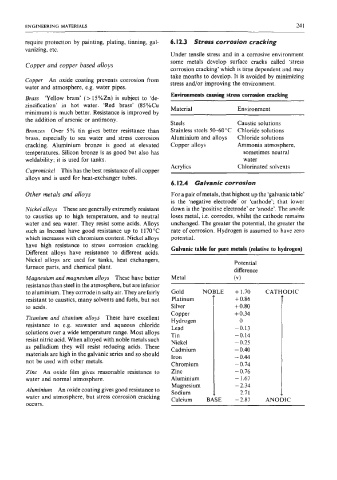
6.12.4 Galvanic corrosion
Other metals and alloys For a pair of metals, that highest up the ‘galvanic table’
is the ‘negative electrode’ or ‘cathode’; that lower
Nickel alloys These are generally extremely resistant down is the ‘positive electrode’ or ‘anode’. The anode
to caustics up to high temperature, and to neutral loses metal, i.e. corrodes, whilst the cathode remains
water and sea water. They resist some acids. Alloys unchanged. The greater the potential, the greater the
such as Inconel have good resistance up to 1170 “C rate of corrosion. Hydrogen is assumed to have zero
which increases with chromium content. Nickel alloys potential.
have high resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Galvanic table for pure metals (relative to hydrogen)
Different alloys have resistance to different acids.
Nickel alloys are used for tanks, heat exchangers, Potential
furnace parts, and chemical plant. difference
Magnesium and magnesium alloys These have better Metal (v 1
resistance than steel in the atmosphere, but are inferior
to aluminium. They corrode in salty air. They are fairly + +1.70 CAT1 ODIC
resistant to caustics, many solvents and fuels, but not Platinum f0.86
to acids. Silver + 0.80
Copper +0.34
Titanium and titanium alloys These have excellent Hydrogen 0
resistance to e.g. seawater and aqueous chloride Lead -0.13
solutions over a wide temperature range. Most alloys Tin -0.14
resist nitric acid. When alloyed with noble metals such Nickel -0.25
as palladium they will resist reducing acids. These Cadmium - 0.40
materials are high in the galvanic series and so should Iron - 0.44
not be used with other metals.
Chromium -0.74
Zinc An oxide film gives reasonable resistance to Zinc -0.76
water and normal atmosphere. Aluminium - 1.67
Magnesium -2.34
Aluminium An oxide coating gives good resistance to Sodium - - 2.7 1
water and atmosphere, but stress corrosion cracking -2.87 AN0 ,IC
occurs.