Page 250 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 250
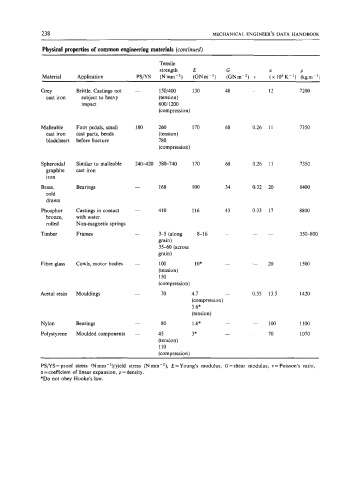
238 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
Physical properties of common engineering materials (continued)
Tensile
strength E G a P
Material Application PS/YS (Nmm-’) (GNm-’) (GNm-’) v (x 1O6K-*) (kgm-3)
Grey Brittle. Castings not - 150/400 130 48 - 12 7200
cast iron subject to heavy (tension)
impact 600/1200
(compression)
Malleable Foot pedals, small 180 260 170 68 0.26 11 7350
cast iron cast parts, bends (tension)
blackheart before fracture 780
(compression)
Spheroidal Similar to malleable 240-420 380-740 170 68 0.26 11 7350
graphite cast iron
iron
Brass, Bearings - 168 100 34 0.32 20 8400
cold
drawn
Phosphor Castings in contact 410 116 43 0.33 17 8800
bronze, with water.
rolled Nonmagnetic springs
Timber Frames - 3-5 (along 8-16 - _ - 350-800
grain)
35-60 (across
grain)
Fibre glass Cowls. motor bodies - 100 10. - - 20 1500
(tension)
150
(compression)
Acetal resin Mouldings - 70 4.7 - 0.35 13.5 1420
(compression)
3.6*
(tension)
Nylon Bearings - 80 1.6* __ - 100 1100
Polystyrene Moulded components - 45 3* - - 70 1070
(tension)
110
(compression)
PS/YS = proof stress (N mm-’)/yield stress (N mm-’), E = Young’s modulus, G = shear modulus, v = Poisson’s ratio,
a =coefficient of linear expansion, p =density.
*Do not obey Hooke’s law.