Page 245 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 245
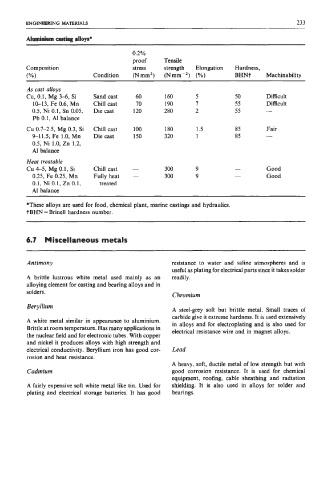
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 233
Almnih crdiag aUoys*
0.2%
proof Tensile
Composition stress strength Elongation Hardness,
(Yo) Condition (Nmm2) (Nmm-2) (%) BHNt Machinability
As cast alloys
Cu, 0.1, Mg 3-6, Si Sand cast 60 160 5 50 Difficult
10-13, Fe 0.6, Mn Chill cast IO 190 7 55 Difficult
0.5, Ni 0.1, Sn 0.05, Die cast 120 280 2 55 -
Pb 0.1, AI balance
Cu 0.7-2.5, Mg 0.3, Si Chill cast 100 180 1.5 85 Fair
9-1 1.5, Fe 1.0, Mn Die cast 150 320 1 85 -
0.5, Ni 1.0, Zn 1.2,
A1 balance
Heat treatable
Cu 4-5, Mg 0.1, Si Chill cast - 300 9 - Good
0.25, Fe 0.25, Mn Fully heat - 300 9 - Good
0.1, Ni 0.1, Zn 0.1, treated
AI balance
*These alloys are used for food, chemical plant, marine castings and hydraulics.
tBHN = Brinell hardness number.
6.7 Miscellaneous metals
Antimony resistance to water and saline atmospheres and is
useful as plating for electrical parts since it takes solder
A brittle lustrous white metal used mainly as an readily.
alloying element for casting and bearing alloys and in
solders. Chromium
Beryllium A steel-grey soft but brittle metal. Small traces of
carbide give it extreme hardness. It is used extensively
A white metal similar in appearance to aluminium. in alloys and for electroplating and is also used for
Brittle at room temperature. Has many applications in electrical resistance wire and in magnet alloys.
the nuclear field and for electronic tubes. With copper
and nickel it produces alloys with high strength and
electrical conductivity. Beryllium iron has good cor- Lead
rosion and heat resistance.
A heavy, soft, ductile metal of low strength but with
Cadmium good corrosion resistance. It is used for chemical
equipment, roofing, cable sheathing and radiation
A fairly expensive soft white metal like tin. Used for shielding. It is also used in alloys for solder and
plating and electrical storage batteries. It has good bearings.