Page 249 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 249
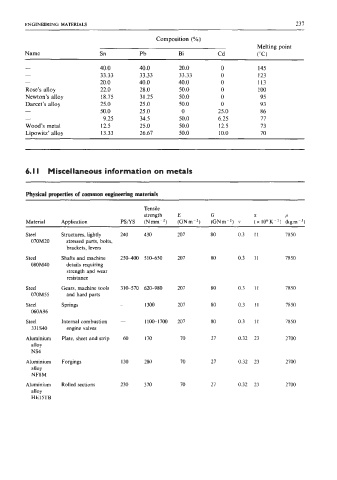
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 237
Composition (%)
Melting point
Name Sn Pb Bi Cd (“C)
- 40.0 40.0 20.0 0 145
- 33.33 33.33 33.33 0 123
- 20.0 40.0 40.0 0 113
Rose’s alloy 22.0 28.0 50.0 0 100
Newton’s alloy 18.75 31.25 50.0 0 95
Darcet’s alloy 25.0 25.0 50.0 0 93
- 50.0 25.0 0 25.0 86
- 9.25 34.5 50.0 6.25 77
Wood’s metal 12.5 25.0 50.0 12.5 73
Lipowitz’ alloy 13.33 26.67 50.0 10.0 70
6. I I Miscellaneous information on metals
~ ~~
Physical properties of common engineering materials
Tensile
strength E G U P
Material Application PS/YS (Nmm-2) (GNm-’) (GNm-2) v (x 106K-’) (kg~~-~)
Steel Structures, lightly 240 430 207 80 0.3 11 7850
070M20 stressed parts, bolts,
brackets, levers
Steel Shafts and machine 25MOO 510-650 207 80 0.3 11 7850
080M40 details requiring
strength and wear
resistance
Steel Gears, machine tools 31&570 620-980 207 80 0.3 I I 7850
070M55 and hard parts
Steel Springs - 1300 207 80 0.3 11 7850
060A96
Steel Internal combustion - 11W17OO 207 80 0.3 11 7850
331340 engine valves
Aluminium Plate, sheet and strip 60 170 70 27 0.32 23 2700
alloy
NS4
Aluminium Forgings 130 280 70 27 0.32 23 2700
alloy
NF8M
Aluminium Rolled sections 230 3 70 70 27 0.32 23 2700
alloy
HE 15TB