Page 243 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 243
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 23 1
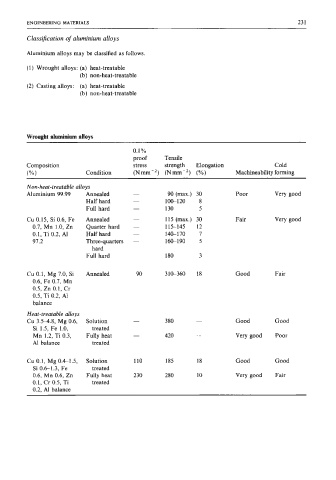
Classification of aluminium alloys
Aluminium alloys may be classified as follows.
(1) Wrought alloys: (a) heat-treatable
(b) non-heat-treatable
(2) Casting alloys: (a) heat-treatable
(b) non-heat-treatable
Wrought aluminium alloys
0.1 Yo
proof Tensile
Composition stress strength Elongation Cold
(%) Condition (Nmm-’) (Nmm-’) (X) Machineability forming
Non-heat-treatable alloys
Aluminium 99.99 Annealed - 90 (max.) 30 Poor Very good
Half hard - 100-120 8
Full hard - 130 5
Cu 0.15, Si 0.6, Fe Annealed - 115 (max.) 30 Fair Very good
0.7, Mn 1.0, Zn Quarter hard - 115-145 12
0.1, Ti 0.2, A1 Half hard - 140-170 7
97.2 Three-quarters - 16190 5
hard
Full hard 180 3
Cu 0.1, Mg 7.0, Si Annealed 90 3 le360 18 Good Fair
0.6, Fe 0.7, Mn
0.5, Zn 0.1, Cr
0.5, Ti 0.2, A1
balance
Heat-treatable alloys
Cu 3.548, Mg 0.6, Solution - 380 - Good Good
Si 1.5, Fe 1.0, treated
Mn 1.2, Ti 0.3, Fully heat - 420 - Very good Poor
AI balance treated
Cu 0.1, Mg 0.4-1.5, Solution 110 185 18 Good Good
Si 0.6-1.3, Fe treated
0.6, Mn 0.6, Zn Fully heat 230 280 10 Very good Fair
0.1, Cr 0.5, Ti treated
0.2, AI balance