Page 239 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 239
ENGINEERING MATERULS 227
6.4.3 Proprties of typical types (contihued)
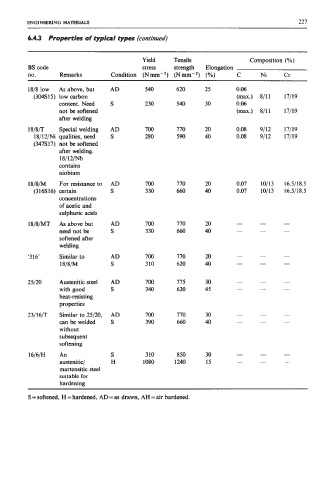
Yield Tensile Composition (YO)
BS code stress strength Elongation
no. Remarks Condition (Nmm-*) (Nmm-’) (%) C Ni Cr
1818 low As above, but AD 540 620 25 0.06
(304S15) low carbon (max.) 8/11 17/19
content. Need S 230 540 30 0.06
not be softened (max.) 8/11 17/19
after welding
18/8/r Special welding AD 700 770 20 0.08 9/12 17/19
18/12/Ni qualities, need S 280 590 40 0.08 9/12 17/19
(347317) not be softened
after welding.
18/12/Nb
contains
niobium
18/8/M For resistance to AD 700 770 20 0.07 10113 16.5/18.5
(316S16) certain S 330 660 40 0.07 10113 16.5/18.5
concentrations
of acetic and
sulphuric acids
18/8/MT As above but AD 700 770 20 - - -
need not be S 330 660 40 - - -
softened after
welding
‘316’ Similar to AD 700 770 20 - - -
18/8/M S 310 620 40 - - -
25/20 Austenitic steel AD 700 775 30 - - -
with good S 340 620 45 - - -
heat-resisting
properties
231 16/T Similar to 25/20, AD 700 770 30 - - -
canbewelded S 390 660 40 - - -
without
subsequent
softening
16/6/H An S 310 850 30 - - -
austenitic/ H 1080 1240 15 - - -
martensitic steel
suitable for
hardening -
S = softened, H =hardened, AD = as drawn, AH =air hardened.