Page 238 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 238
226 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
6.4.3 Properties of typical types
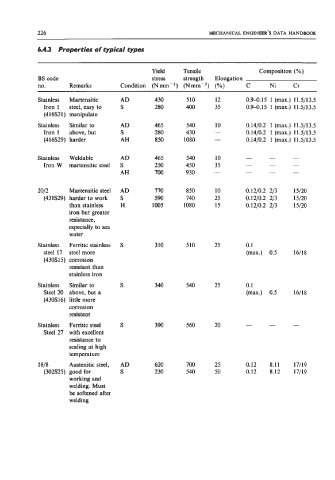
Yield Tensile Composition (YO)
BS code stress strength Elongation
no. Remarks Condition (Nmm-2) (Nmrn-?) (YO) C Ni Cr
Stainless Martensitic AD 430 5 10 12 0.9-0.15 1 (max.) 11.5/13.5
Iron 1 steel, easy to S 280 400 35 0.9-0.15 1 (max.) 11.5/13.5
(416821) manipulate
Stainless Similar to AD 465 540 10 0.14/0.2 1 (max.) 11.5/13.5
Iron 1 above, but S 280 430 - 0.1410.2 1 (max.) 11.51133
(416829) harder AH 850 1080 - 0.14/0.2 1 (max.) 11.5/13.5
Stainless Weldable AD 465 540 10 - - -
Iron W martensitic steel S 250 450 35 - - -
AH 700 930 - - - -
2012 Martensitic steel AD 770 850 10 0.1210.2 213 15/20
(43 1S29) harder to work S 590 740 25 0.1210.2 213 15/20
than stainless H 1005 1080 15 0.1210.2 213 15/20
iron but greater
resistance,
especially to sea
water
Stainless Ferritic stainless S 310 510 25 0.1
steel 17 steel more (max.) 0.5 16/18
(430S15) corrosion
resistant than
stainless iron
Stainless Similar to S 340 540 25 0.1
Steel 20 above, but a (max.) 0.5 16/18
(430316) little more
corrosion
resistant
Stainless Ferritic steel S 390 560 20 - - -
Steel 27 with excellent
resistance to
scaling at high
temperature
1818 Austenitic steel, AD 620 700 25 0.12 8.11 17/19
(302325) good for S 230 540 50 0.12 8.12 17/19
working and
welding. Must
be softened after
welding