Page 233 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 233
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 22 1
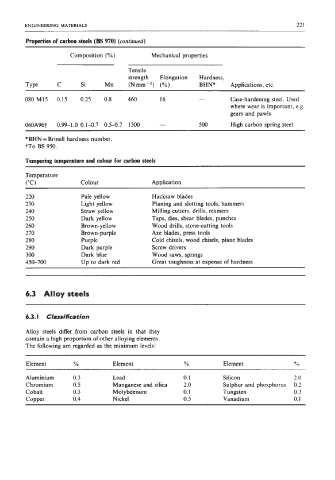
Properties of carbon steels (E 970) (continued)
Composition (YO) Mechanical properties
Tensile
strength Elongation Hardness,
Type C Si Mn (Nmm-*) (YO) BHN* Applications, etc.
080 M15 0.15 0.25 0.8 460 16 - Case-hardening steel. Used
where wear is important, e.g.
gears and pawls
060A96t 0.99-1.0 0.14.7 0.5-0.7 1300 - 500 High carbon spring steel
*BHN =Brinell hardness number.
tTo BS 950.
Tempering temperature and clolour for carbon steels
Temperature
("C) Colour Application
_____~
220 Pale yellow Hacksaw blades
230 Light yellow Planing and slotting tools, hammers
240 Straw yellow Milling cutters, drills, reamers
250 Dark yellow Taps, dies, shear blades, punches
260 Brown-yellow Wood drills, stone-cutting tools
270 Brown-purple Axe blades, press tools
280 Purple Cold chisels, wood chisels, plane blades
290 Dark purple Screw drivers
300 Dark blue Wood saws, springs
450-700 Up to dark red Great toughness at expense of hardness
6.3 Alloy steels
6.3. I Classification
Alloy steels differ from carbon steels in that they
contain a high proportion of other alloying elements.
The following are regarded as the minimum levels:
Element YO Element YO Element O/Q
Aluminium 0.3 Lead 0.1 Silicon 2 .o
Chromium 0.5 Manganese and silica 2.0 Sulphur and phosphorus 0.2
Cobalt 0.3 Molybdenum 0.1 Tungsten 0.3
Copper 0.4 Nickel 0.5 Vanadium 0.1