Page 231 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 231
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 219
6. I .3 Malleable irons
These have excellent machining qualities with strength black heart with superior machining properties; and
similar to grey irons but better ductility as a result of pearlitic which is superior to the other two but difficult
closely controlled heat treatment. There are three to produce.
types: white heart with superior casting properties;
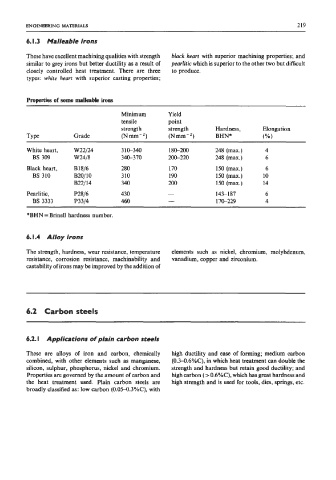
Properties of some maUeabie irons
Minimum Yield
tensile point
strength strength Hardness, Elongation
Type Grade (Nmm-2) (Nmm-2) BHN* (%)
White heart, W22/24 310-340 180-200 248 (max.) 4
BS 309 W24/8 340-370 200-220 248 (max.) 6
Black heart, B18/6 280 170 150 (max.) 6
BS 310 B20/10 3 10 190 150 (max.) 10
B22/14 340 200 150 (max.) 14
Pearlitic, P28/6 430 - 143-187 6
BS 3333 P33/4 460 - 170-229 4
*BHN = Brinell hardness number.
6. I .4 Alloy irons
The strength, hardness, wear resistance, temperature elements such as nickel, chromium, molybdenum,
resistance, corrosion resistance, machinability and vanadium, copper and zirconium.
castability of irons may be improved by the addition of
6.2 Carbon steels
6.2. I Applications of plain carbon steels
These are alloys of iron and carbon, chemically high ductility and ease of forming; medium carbon
combined, with other elements such as manganese, (0.3-0.6%C), in which heat treatment can double the
silicon, sulphur, phosphorus, nickel and chromium. strength and hardness but retain good ductility; and
Properties are governed by the amount of carbon and high carbon (> 0.6%C), which has great hardness and
the heat treatment used. Plain carbon steels are high strength and is used for tools, dies, springs, etc.
broadly classified as: low carbon (0.05-0.3%C), with