Page 236 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 236
224 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
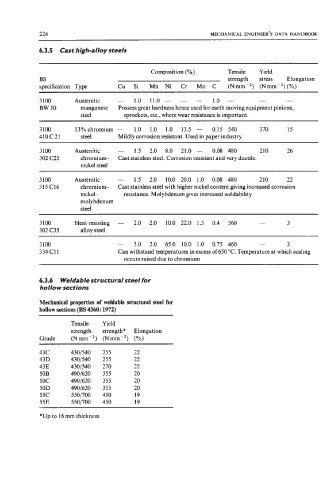
6.3.5 Cast high-alloy steels
Composition (YO) Tensile Yield
BS strength stress Elongation
specification Type Cu Si Mn Ni Cr Mo C (Nmm-’) (Nmm-’)(%)
3 100 Austenitic - 1.0 11.0 - - - 1.0 - - -
BW 10 manganese Possess great hardness hence used for earth moving equipment pinions,
steel sprockets, etc., where wear resistance is important.
3 100 13%chromium - 1.0 1.0 1.0 13.5 - 0.15 540 3 70 15
410 C 21 steel Mildly corrosion resistant. Used in paper industry
3100 Austenitic - 1.5 2.0 8.0 21.0 - 0.08 480 210 26
302 C25 chromium- Cast stainless steel. Corrosion resistant and very ductile.
nickel steel
3100 Austenitic - 1.5 2.0 10.0 20.0 1.0 0.08 480 210 22
315 C16 chromium- Cast stainless steel with higher nickel content giving increased corrosion
nickel- resistance. Molybdenum gives increased weldability
molybdenum
steel
3 100 Heat-resisting - 2.0 2.0 10.0 22.0 1.5 0.4 560 - 3
302 C35 alloy steel
3100 - 3.0 2.0 65.0 10.0 1.0 0.75 460 - 3
334Cll Can withstand temperatures in excess of 650 “C. Temperature at which scaling
occurs raised due to chromium
6.3.6 Weldable structural steel for
hollow sections
Mechanical properties of weldable structural steel for
hollow sections (BS 4360: 1972)
Tensile Yield
strength strength* Elongation
Grade (Nmm-’) (Nmm-’) (YO)
43c 4301540 255 22
43D 4301540 255 22
43E 4301540 270 22
50B 4901620 355 20
5oc 4901620 355 20
50D 4901620 355 20
55c 550/700 450 19
55E 5501700 450 19
*Up to 16mm thickness.