Page 232 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 232
220 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
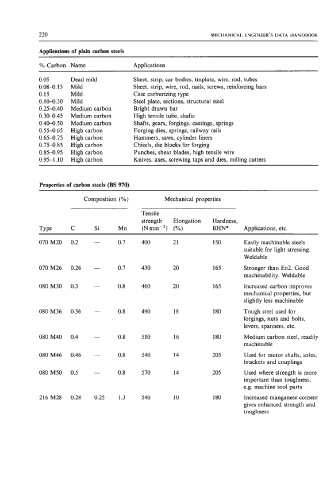
Applications of plain carbon steels
%Carbon Name Applications
0.05 Dead mild Sheet, strip, car bodies, tinplate, wire, rod, tubes
0.084. 15 Mild Sheet, strip, wire, rod, nails, screws, reinforcing bars
0.15 Mild Case carburizing type
0.10-0.30 Mild Steel plate, sections, structural steel
0.254.40 Medium carbon Bright drawn bar
0.30-0.45 Medium carbon High tensile tube, shafts
0.40-0.50 Medium carbon Shafts, gears, forgings, castings, springs
0.554.65 High carbon Forging dies, springs, railway rails
0.654.75 High carbon Hammers, saws, cylinder liners
0.75-0.85 High carbon Chisels, die blocks for forging
0.854.95 High carbon Punches, shear blades, high tensile wire
0.95-1.10 High carbon Knives, axes, screwing taps and dies, milling cutters
Properties of carbon steels (BS 970)
Composition (%) Mechanical properties
Tensile
strength Elongation Hardness,
Type C Si Mn (Nmm-’) (%) BHN* Applications, etc.
070 M20 0.2 - 0.7 400 21 150 Easily machinable steels
suitable for light stressing.
Weldable
070 M26 0.26 - 0.7 430 20 165 Stronger than En2. Good
machinability. Weldable
080 M30 0.3 - 0.8 460 20 165 Increased carbon improves
mechanical properties, but
slightly less machinable
080 M36 0.36 - 0.8 490 18 180 Tough steel used for
forgings, nuts and bolts,
levers, spanners, etc.
080 M40 0.4 - 0.8 510 16 180 Medium carbon steel, readily
machinable
080 M46 0.46 - 0.8 540 14 205 Used for motor shafts, axles,
brackets and couplings
080 M5O 0.5 - 0.8 570 14 205 Used where strength is more
important than toughness,
e.g. machine tool parts
216 M28 0.28 0.25 1.3 540 10 180 Increased manganese content
gives enhanced strength and
toughness