Page 270 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 270
258 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
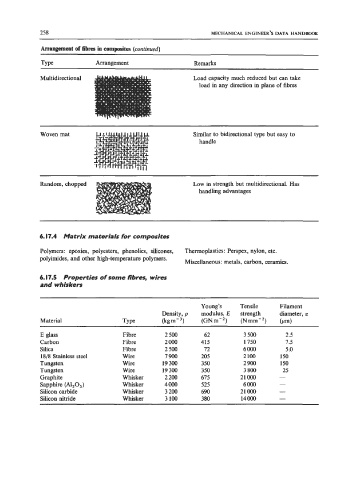
Arrangement of fibres in composites (continued)
Type Arrangement Remarks
Multidirectional Load capacity much reduced but can take
load in any direction in plane of fibres
Random, chopped Low in strength but multidirectional. Has
handling advantages
6.17.4 Matrix materials for composites
Polymers: epoxies, polyesters, phenolics, silicones, Thermoplastics: Perspex, nylon, etc.
polyimides, and other high-temperature polymers.
Miscellaneous: metals, carbon, ceramics.
6.17.5 Properties of some fibres, wires
and whiskers
Young’s Tensile Filament
Density, p modulus, E strength diameter, GL
Material Type (kgm-j) (GNm-’) (Nmm-2) (pm)
E glass Fibre 2 500 62 3 500 2.5
Carbon Fibre 2000 415 1750 7.5
Silica Fibre 2 500 72 6000 5.0
18/8 Stainless steel Wire 7900 205 2 100 150
Tungsten Wire 19 300 350 2900 150
Tungsten Wire 19 300 350 3 800 25
Graphite Whisker 2 200 675 21 000
Sapphire (A1 0,) Whisker 4000 525 6000
Silicon carbide Whisker 3 200 690 21 000
Silicon nitride Whisker 3 100 380 14000