Page 269 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 269
ENGINEERING MATERIALS 251
6.17 Composites
A composite is a material consisting of two (or more) forcing rods. Vehicle tyres consist of rubber reinforced
different materials bonded together, one forming a with woven cords.
‘matrix’ in which are embedded fibres or particles that Plastics are reinforced with glass, carbon and other
increase the strength and stiffness of the matrix fibres. The fibres may be unidirectional, woven or
material. random chopped. Metals, carbon and ceramics are
A natural composite is wood in which cellulose also used as matrix materials.
fibres are embedded in a lignin matrix. Concrete is a So-called ‘whiskers’, which are single crystals of
composite in which particles of stone add strength with silicon carbide, silicon nitride, sapphire, etc., give
a further increase in strength provided by steel rein- extremely high strength.
6.17. I Elastic modulus of a composite 6.17.2 Acronyms for composites
(continuous fibres in direction of load)
FRP Fibre-reinforced plastic
Let: FRT Fibre-reinforced thermoplastic
E, = modulus of fibres GRP Glass-reinforced plastic
E, =modulus of matrix GRC Glass-reinforced composite
E, = modulus of composite CFC Carbon fibre composite
CFRP Carbon-fibre-reinforced plastic
r = (cross-sectional area of fibres)/(total cross- CFRT Carbon-fibre-reinforced thermoplastic
sectional area)
E,=rE,+(l-r)E, 6.17.3 Forms of fibres for composites
Fibre: length over 10 times the diameter; diameter less
than 0.25 mm.
Filament: a continuous fibre.
Wire: a metallic fibre
Whisker: a fibre consisting of a single crystal.
Matrix with fibres
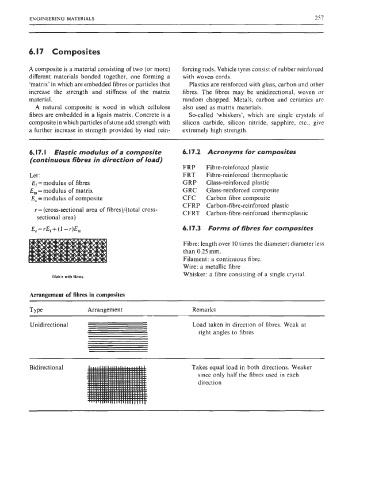
Arrangement of fibres in composites
Type Arrangement Remarks
Unidirectional Load taken in direction of fibres. Weak at
right angles to fibres
Takes equal load in both directions. Weaker
since only half the fibres used in each
direction