Page 272 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 272
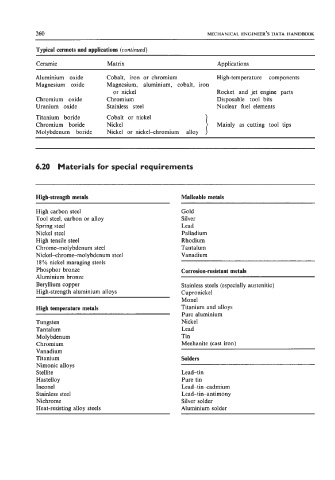
260 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
Typical cermets and applications (continued)
Ceramic Matrix Applications
Aluminium oxide Cobalt, iron or chromium High-temperature components
Magnesium oxide Magnesium, aluminium, cobalt, iron
or nickel Rocket and jet engine parts
Chromium oxide Chromium Disposable tool bits
Uranium oxide Stainless steel Nuclear fuel elements
Titanium boride Cobalt or nickel
Chromium boride Nickel Mainly as cutting tool tips
Molybdenum boride Nickel or nickel-chromium alloy
6.20 Materials for special requirements
High-strength metals Malleable metals
High carbon steel Gold
Tool steel, carbon or alloy Silver
Spring steel Lead
Nickel steel Palladium
High tensile steel Rhodium
Chrome-molybdenum steel Tantalum
Nickekhrome-molybdenum steel Vanadium
18% nickel maraging steels
Phosphor bronze Corrosion-resistant metals
Aluminium bronze
Beryllium copper Stainless steels (especially austenitic)
High-strength aluminium alloys Cupronickel
Monel
High temperature metals Titanium and alloys
Pure aluminium
Tungsten Nickel
Tantalum Lead
Molybdenum Tin
Chromium Meehanite (cast iron)
Vanadium
Titanium Solders
Nimonic alloys
Stellite Lead-tin
Hastelloy Pure tin
Inconel Lead-tinxadmium
Stainless steel Lead-tin-antimon y
Nichrome Silver solder
Heat-resisting alloy steels Aluminium solder