Page 276 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 276
264 MECHANICAL ENGINEER'S DATA HANDBOOK
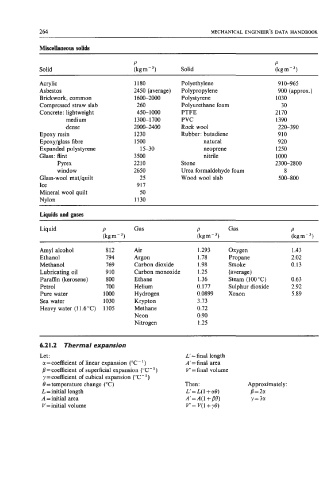
Miscellaneous solids
Solid
Acrylic 1180 Polyethylene 910-965
Asbestos 2450 (average) Polypropylene 900 (approx.)
Brickwork, common 1600-2000 Polystyrene 1030
Compressed straw slab 260 Polyurethane foam 30
Concrete: lightweight 45&1000 PTFE 2170
medium 1300-1700 PVC 1390
dense 2000-2400 Rock wool 220-390
Epoxy resin 1230 Rubber: butadiene 910
Epoxy/glass fibre 1500 natural 920
Expanded polystyrene 15-30 neoprene 1250
Glass: flint 3500 nitrile 1000
Pyrex 2210 Stone 2300-2800
window 2650 Urea formaldehyde foam 8
Glass-wool mat/quilt 25 Wood wool slab 500-800
Ice 917
Mineral wool quilt 50
Nylon 1130
Liquids and gases
Liquid P Gas P Gas P
(kgm-3) (kgm-3) (kgm-3)
Amyl alcohol 812 Air 1.293 Oxygen 1.43
Ethanol 794 Argon 1.78 Propane 2.02
Methanol 769 Carbon dioxide 1.98 Smoke 0.13
Lubricating oil 910 Carbon monoxide 1.25 (average)
Paraffin (kerosene) 800 Ethane 1.36 Steam (100 "C) 0.63
Petrol 700 Helium 0.177 Sulphur dioxide 2.92
Pure water lo00 Hydrogen 0.0899 Xenon 5.89
Sea water 1030 Krypton 3.73
Heavy water (1 1.6 "C) 1105 Methane 0.72
Neon 0.90
Nitrogen 1.25
6.2 I .2 Thermal expansion
Let: L' = final length
tl =coefficient of linear expansion ("C- l) A'=final area
,!?=coefficient of superficial expansion ("C- I) V" = final volume
y=coefficient of cubical expansion ("C-')
0 =temperature change ("C) Then: Approximately :
L = initial length L'=L(I +tie) ,!?=2a
A =initial area A'=A(I+~) y=3a
V= initial volume v= v(i+ye)