Page 281 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 281
ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS 269
7. I .6 Gauge blocks (slip gauges) 7. I .7 Measurement of large bores
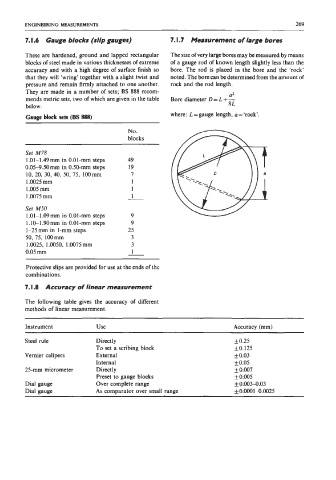
These are hardened, ground and lapped rectangular The size of very large bores may be measured by means
blocks of steel made in various thicknesses of extreme of a gauge rod of known length slightly less than the
accuracy and with a high degree of surface finish so bore. The rod is placed in the bore and the ‘rock’
that they will ‘wring’ together with a slight twist and noted. The bore can be determined from the amount of
pressure and remain firmly attached to one another. rock and the rod length.
They are made in a number of sets; BS 888 recom-
a’
mends metric sets, two of which are given in the table Bore diameter D = L + -
below. 8L
where: L = gauge length, a = ‘rock’.
Gauge Mock sets (BS 888)
No.
blocks
Set M78
1.01-1.49mm in 0.01-mm steps 49
0.05-9.50mm in 0.50-mm steps 19
10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 75, l00mm 7
1.0025 mm 1
1.005 mm 1
1.0075 mm -
1
Set M50
1.01-1.Wmm in 0.01-mm steps 9
1.10-1.90mm in 0.01-mm steps 9
1-25 mm in 1-mm steps 25
50, 75, l00mm 3
1.0025, 1.0050, 1.0075 mm 3
1
0.05 mm -
Protective slips are provided for use at the ends of the
combinations.
7. I .8 Accuracy of linear measurement
The following table gives the accuracy of different
methods of linear measurement.
Instrument Use Accuracy (mm)
Steel rule Directly f 0.25
To set a scribing block k0.125
Vernier calipers External k 0.03
Internal +_ 0.05
25-mm micrometer Directly f 0.007
Preset to gauge blocks k 0.005
Dial gauge Over complete range f 0.003-0.03
Dial gauge As comparator over small range fO.ooO1-0.0025