Page 283 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 283
272 Furnaces
1
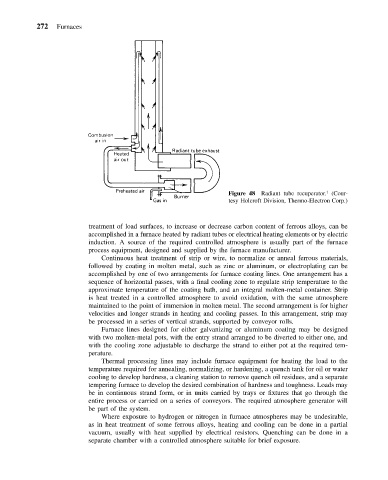
Figure 48 Radiant tube recuperator. (Cour-
tesy Holcroft Division, Thermo-Electron Corp.)
treatment of load surfaces, to increase or decrease carbon content of ferrous alloys, can be
accomplished in a furnace heated by radiant tubes or electrical heating elements or by electric
induction. A source of the required controlled atmosphere is usually part of the furnace
process equipment, designed and supplied by the furnace manufacturer.
Continuous heat treatment of strip or wire, to normalize or anneal ferrous materials,
followed by coating in molten metal, such as zinc or aluminum, or electroplating can be
accomplished by one of two arrangements for furnace coating lines. One arrangement has a
sequence of horizontal passes, with a final cooling zone to regulate strip temperature to the
approximate temperature of the coating bath, and an integral molten-metal container. Strip
is heat treated in a controlled atmosphere to avoid oxidation, with the same atmosphere
maintained to the point of immersion in molten metal. The second arrangement is for higher
velocities and longer strands in heating and cooling passes. In this arrangement, strip may
be processed in a series of vertical strands, supported by conveyor rolls.
Furnace lines designed for either galvanizing or aluminum coating may be designed
with two molten-metal pots, with the entry strand arranged to be diverted to either one, and
with the cooling zone adjustable to discharge the strand to either pot at the required tem-
perature.
Thermal processing lines may include furnace equipment for heating the load to the
temperature required for annealing, normalizing, or hardening, a quench tank for oil or water
cooling to develop hardness, a cleaning station to remove quench oil residues, and a separate
tempering furnace to develop the desired combination of hardness and toughness. Loads may
be in continuous strand form, or in units carried by trays or fixtures that go through the
entire process or carried on a series of conveyors. The required atmosphere generator will
be part of the system.
Where exposure to hydrogen or nitrogen in furnace atmospheres may be undesirable,
as in heat treatment of some ferrous alloys, heating and cooling can be done in a partial
vacuum, usually with heat supplied by electrical resistors. Quenching can be done in a
separate chamber with a controlled atmosphere suitable for brief exposure.