Page 366 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 366
5 Other Types of Heat Pipes 355
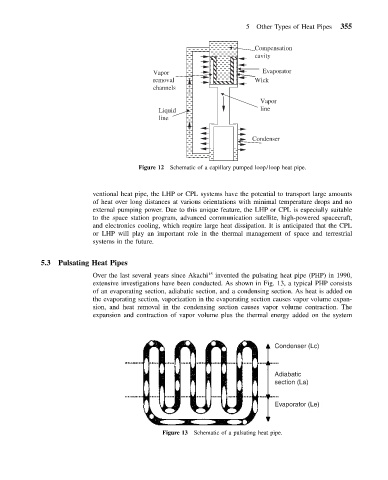
Compensation
cavity
Vapor Evaporator
removal Wick
channels
Vapor
Liquid line
line
Condenser
Figure 12 Schematic of a capillary pumped loop/loop heat pipe.
ventional heat pipe, the LHP or CPL systems have the potential to transport large amounts
of heat over long distances at various orientations with minimal temperature drops and no
external pumping power. Due to this unique feature, the LHP or CPL is especially suitable
to the space station program, advanced communication satellite, high-powered spacecraft,
and electronics cooling, which require large heat dissipation. It is anticipated that the CPL
or LHP will play an important role in the thermal management of space and terrestrial
systems in the future.
5.3 Pulsating Heat Pipes
Over the last several years since Akachi 15 invented the pulsating heat pipe (PHP) in 1990,
extensive investigations have been conducted. As shown in Fig. 13, a typical PHP consists
of an evaporating section, adiabatic section, and a condensing section. As heat is added on
the evaporating section, vaporization in the evaporating section causes vapor volume expan-
sion, and heat removal in the condensing section causes vapor volume contraction. The
expansion and contraction of vapor volume plus the thermal energy added on the system
Condenser (Lc)
Adiabatic
section (La)
Evaporator (Le)
Figure 13 Schematic of a pulsating heat pipe.