Page 415 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 415
404 Cooling Electronic Equipment
The matrix [ ] is called the thermal transmission matrix and provides a linear transfor-
mation from tip to base conditions. It has been cataloged for all of the common fin
shapes. 38–40 For the longitudinal fin of rectangular profile
[ ] cosh mb 1 0
sinh mb
Y sinh mb Y cosh mb (87)
0
and this matrix possesses an inverse called the inverse thermal transmission matrix
cosh mb 1 0
sinh mb
[ ] [ ] 1 Y (88)
Y sinh mb cosh mb
0
The assembly of fins into an array may require the use of any or all of three
algorithms. 40–42 The objective is to determine the input admittance of the entire array
Y
q
b
in (89)
b A
which can be related to the array (fin) efficiency by
Y
in (90)
f
hA ƒ
The determination of Y can involve as many as three algorithms for the combination
in
of individual fins into an array.
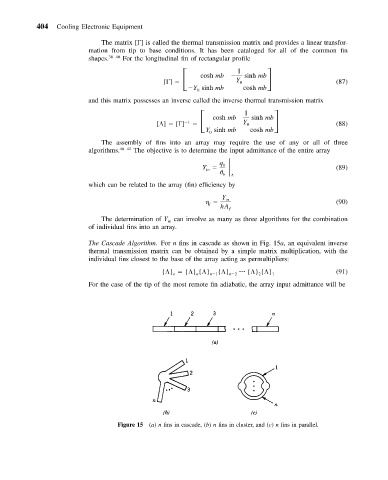
The Cascade Algorithm. For n fins in cascade as shown in Fig. 15a, an equivalent inverse
thermal transmission matrix can be obtained by a simple matrix multiplication, with the
individual fins closest to the base of the array acting as permultipliers:
{ } { }{ } n 1 { } n 2 { }{ } 1 (91)
n
e
2
For the case of the tip of the most remote fin adiabatic, the array input admittance will be
Figure 15 (a) n fins in cascade, (b) n fins in cluster, and (c) n fins in parallel.