Page 125 - Singiresu S. Rao-Mechanical Vibrations in SI Units, Global Edition-Pearson (2017)
P. 125
122 Chapter 1 Fundamentals oF Vibration
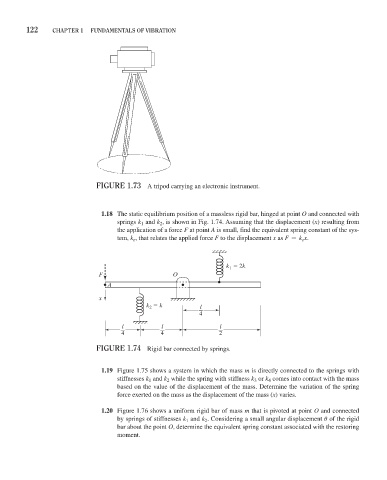
FiGure 1.73 A tripod carrying an electronic instrument.
1.18 The static equilibrium position of a massless rigid bar, hinged at point O and connected with
springs k 1 and k 2 , is shown in Fig. 1.74. Assuming that the displacement (x) resulting from
the application of a force F at point A is small, find the equivalent spring constant of the sys-
tem, k e , that relates the applied force F to the displacement x as F = k e x.
k 2k
1
F O
A
x
k 2 k l
4
l l l
4 4 2
FiGure 1.74 Rigid bar connected by springs.
1.19 Figure 1.75 shows a system in which the mass m is directly connected to the springs with
stiffnesses k 1 and k 2 while the spring with stiffness k 3 or k 4 comes into contact with the mass
based on the value of the displacement of the mass. Determine the variation of the spring
force exerted on the mass as the displacement of the mass (x) varies.
1.20 Figure 1.76 shows a uniform rigid bar of mass m that is pivoted at point O and connected
by springs of stiffnesses k 1 and k 2 . Considering a small angular displacement u of the rigid
bar about the point O, determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring
moment.