Page 124 - Singiresu S. Rao-Mechanical Vibrations in SI Units, Global Edition-Pearson (2017)
P. 124
problems 121
1.13 A cantilever beam of length L and Young’s modulus E is subjected to a bending force at its
free end. Compare the spring constants of beams with cross sections in the form of a solid
circle (of diameter d), square (of side d), and hollow circle (of mean diameter d and wall
thickness t = 0.1d). Determine which of these cross sections leads to an economical design
for a specified value of bending stiffness of the beam.
1.14 An electronic instrument, weighing 1000 N, is supported on a rubber mounting whose force-
3
deflection relationship is given by F1x2 = 157 x + 0.2 x , where the force (F) and the
deflection (x) are in newtons and millimeters, respectively. Determine the following:
a. Equivalent linear spring constant of the mounting at its static equilibrium position.
b. Deflection of the mounting corresponding to the equivalent linear spring constant.
1.15 The force-deflection relation of a steel helical spring used in an engine is found experi-
3
2
mentally as F1x2 = 34.6 x + 0.34 x + 0.002 x , where the force (F) and deflection (x) are
measured in newtons and millimeters, respectively. If the spring undergoes a steady deflec-
tion of 12.7 mm during the operation of the engine, determine the equivalent linear spring
constant of the spring at its steady deflection.
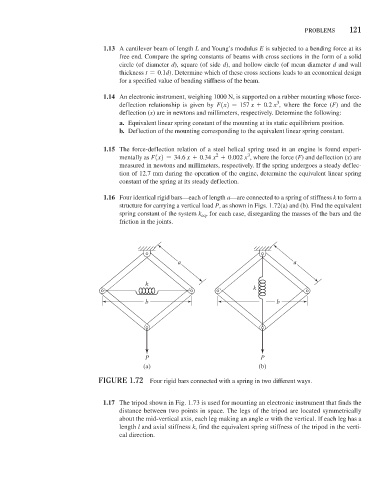
1.16 Four identical rigid bars—each of length a—are connected to a spring of stiffness k to form a
structure for carrying a vertical load P, as shown in Figs. 1.72(a) and (b). Find the equivalent
spring constant of the system k eq , for each case, disregarding the masses of the bars and the
friction in the joints.
a a
k
k
b b
P P
(a) (b)
FiGure 1.72 Four rigid bars connected with a spring in two different ways.
1.17 The tripod shown in Fig. 1.73 is used for mounting an electronic instrument that finds the
distance between two points in space. The legs of the tripod are located symmetrically
about the mid-vertical axis, each leg making an angle a with the vertical. If each leg has a
length l and axial stiffness k, find the equivalent spring stiffness of the tripod in the verti-
cal direction.