Page 112 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 112
Chapter 3. Mechanics of a unidirectional ply 97
a,,MPa
2000 r
1600
1200
800
400
0
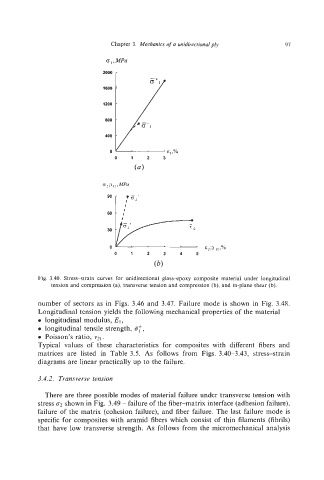
Fig. 3.40. Stress-strain curves for unidirectional glass+poxy composite material under longitudinal
tension and compression (a), transverse tension and compression (b), and in-plane shear (b).
number of sectors as in Figs. 3.46 and 3.47. Failure mode is shown in Fig. 3.48.
Longitudinal tension yields the following mechanical properties of the material
0 longitudinal modulus, El,
0 longitudinal tensile strength, @;C,
0 Poisson’s ratio, v21.
Typical values of these characteristics for composites with different fibers and
matrices are listed in Table 3.5. As follows from Figs. 3.40-3.43, stress-strain
diagrams are linear practically up to the failure.
3.4.2. Transverse tension
There are three possible modes of material failure under transverse tension with
stress 02 shown in Fig. 3.49 -failure of the fiber-matrix interface (adhesion failure),
failure of the matrix (cohesion failure), and fiber failure. The last failure mode is
specific for composites with aramid fibers which consist of thin filaments (fibrils)
that have low transverse strength. As follows from the micromechanical analysis