Page 132 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 132
Chapter 3. Mechanics of a unidirectional ply 1 I7
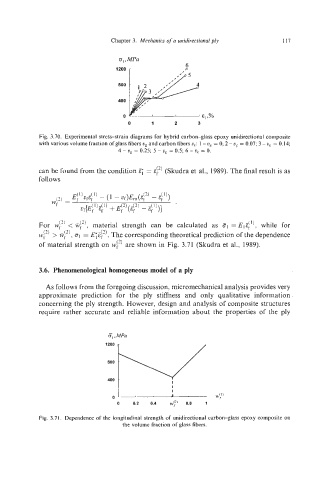
a,,MPa
6
1200
800
400
0 E,,%
0 1 2 3
Fig. 3.70. Experimental stress-strain diagrams for hybrid carbon-glass epoxy unidirectional composite
with various volume fraction of glass fibers ug and carbon fibers u,: 1 - ug = 0; 2 - u, = 0.07; 3 - us = 0.14;
4 - ug = 0.25; 5 - ug = 0.5; 6 - U, = 0.
can be found from the condition = .$) (Skudra et al., 1989). The final result is as
follows
For wi2' < ii~!2), material strength can be calculated as 81=El.$.'), while for
,(2) > ,CTI = ET$). The corresponding theoretical prediction of the dependence
-
f
of material strength on wi2)are shown in Fig. 3.71 (Skudra et al., 1989).
3.6. Phenomenological homogeneous model of a ply
As follows from the foregoing discussion, micromechanical analysis provides very
approximate prediction for the ply stiffness and only qualitative information
concerning the ply strength. However, design and analysis of composite structures
require rather accurate and reliable information about the properties of the ply
5,.MPa
I
Fig. 3.71. Dependence of the longitudinal strength of unidirectional carbon-glass epoxy composite on
the volume fraction of glass fibers.