Page 131 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 131
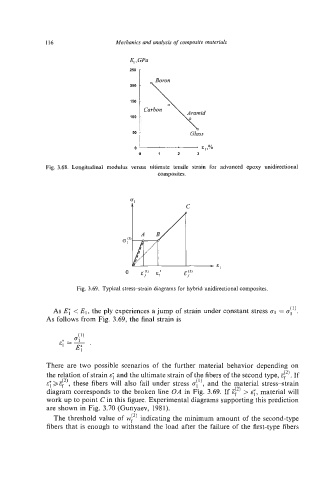
116 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
E,,GPa
2sD r
200 -
150 -
0 1 2 3
Fig. 3.68. Longitudinal modulus versus ultimate tensile strain for advanced epoxy unidirectional
composites.
C
Fig. 3.69. Typical stress-strain diagrams for hybrid unidirectional composites.
As ET < El, the ply experiences a jump of strain under constant stress GI= o1(1) .
As follows from Fig. 3.69, the final strain is
There are two possible scenarios of the further material behavior depending on
the relation of strain ET and the ultimate strain of the fibers of the second type, E?). If
E;~E?), these fibers will also fail under stress oil), and the material stress-strain
diagram corresponds to the broken line OA in Fig. 3.69. If E?) > E:, material will
work up to point C in this figure. Experimental diagrams supporting this prediction
are shown in Fig. 3.70 (Gunyaev, 1981).
The threshold value of indicating the minimum amount of the second-type
fibers that is enough to withstand the load after the failure of the first-type fibers