Page 128 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 128
Chapter 3. Mechanics of a unidirectional ply 113
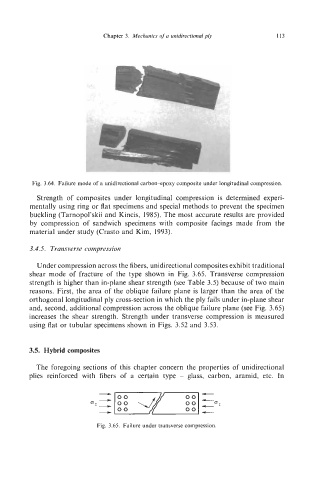
Fig. 3.64. Failure mode of a unidirectional carbon+poxy composite under longitudinal compression.
Strength of composites under longitudinal compression is determined experi-
mentally using ring or flat specimens and special methods to prevent the specimen
buckling (Tarnopol’skii and Kincis, 1985). The most accurate results are provided
by compression of sandwich specimens with composite facings made from the
material under study (Crasto and Kim, 1993).
3.4.5. Transverse compression
Under compression across the fibers, unidirectional composites exhibit traditional
shear mode of fracture of the type shown in Fig. 3.65. Transverse compression
strength is higher than in-plane shear strength (see Table 3.5) because of two main
reasons. First, the area of the oblique failure plane is larger than the area of the
orthogonal longitudinal ply cross-section in which the ply fails under in-plane shear
and, second, additional compression across the oblique failure plane (see Fig. 3.65)
increases the shear strength. Strength under transverse compression is measured
using flat or tubular specimens shown in Figs. 3.52 and 3.53.
3.5. Hybrid composites
The foregoing sections of this chapter concern the properties of unidirectional
plies reinforced with fibers of a certain type - glass, carbon, aramid, etc. In
Fig. 3.65. Failure under transverse compression.