Page 294 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 294
Chapter 6. Fuilure criteria una strength of laminares 219
0,,MPa O,, MPa
I000 1000
500 500
-.
200 200 '. 2 /
0-
~ 7..-
100 100 .......
50
0
0 15 30 45 60 75 90 0 15 30 45 60 75 90
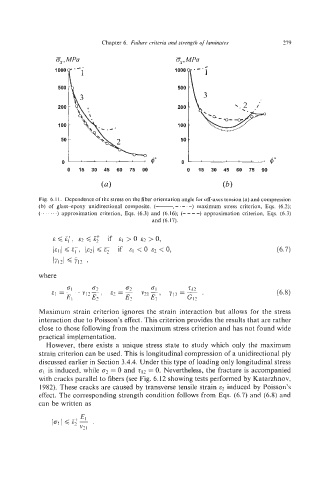
Fig. 6. I 1. Dependence of the stress on the fiber orientationangle fur or-axes tension (a) and compression
(h) of glass-epoxy unidirectional composite. (-, -. -. -) maximum stress criterion, Eqs. (6.2):
(. t. t.. .) approximation criterion, Eqs. (6.3) and (6.16); (- -- -) approximation criterion, Eqs. (6.3)
and (6.17).
where
Maximum strain criterion ignores the strain interaction but allows for the stress
interaction due to Poisson's effect. This criterion provides the results that are rather
close to those following from the maximum stress criterion and has not found wide
practical implementation.
However, there exists a unique stress state to study which only the maximum
strain criterion can be used. This is longitudinal compression of a unidirectional ply
discussed earlier in Section 3.4.4. Under this type of loading only longitudinal stress
CT~is induced, while 02 = 0 and 212 = 0. Nevertheless, the fracture is accompanied
with cracks parallel to fibers (see Fig. 6.12 showing tests performed by Katarzhnov,
1982). These cracks are caused by transverse tensile strain E:! induced by Poisson's
effect. The corresponding strength condition follows from Eqs. (6.7) and (6.8) and
can be written as