Page 325 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 325
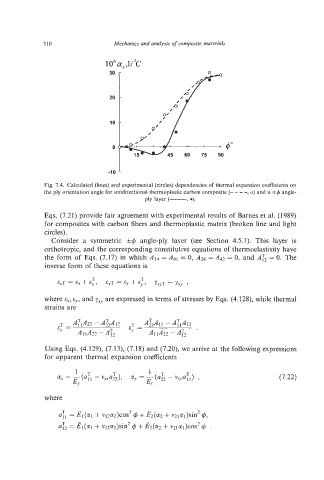
310 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
Fig. 7.4. Calculated (lines) and experimental (circles)dependencies of thermal expansion coefficients on
the ply orientation angle for unidirectional thermoplastic carbon composite (- -- -, 0) and a &4 angle-
ply layer (-, -).
Eqs. (7.21) provide fair agreement with experimental results of Barnes et al. (1989)
for composites with carbon fibers and thermoplastic matrix (broken line and light
circles).
Consider a symmetric angle-ply layer (see Section 4.5.1). This layer is
orthotropic, and the corresponding constitutive equations of thermoelastisity have
the form of Eqs. (7.17) in which A14 = A41 = 0, ,424 =A42 = 0, and AT2 = 0. The
inverse form of these equations is
T
T
&IT= 8.r + Ex , E.,c~ = E? + E,, Y.~!T = Yxj, >
where E.~,E,., and y,,. are expressed in terms of stresses by Eqs. (4.128), while thermal
strains are
Using Eqs. (4.129), (7.13), (7.18) and (7.20), we arrive at the following expressions
for apparent thermal expansion coefficients
(7.22)
where