Page 90 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 90
Chapter 3. Mechanics of a unidirectional ply 15
As a result, Eq. (3.54) yields
2aGmu~(0)sin (0.J2) sin O.,
D,v= (s= 1, 2,3)...)k) . (3.55)
p,(2k sin O,s - sin 2MV)
Substituting these coefficients into Eq. (3.51) we can find uo(O), Le.,
sin(Oi/2) sin Oi )-'
2k sin Oi- sin 2ke1 (3.56)
Thus, the solution for the problem under study is specified with Eqs. (3.44)-(3.50),
(3.55) and (3.56).
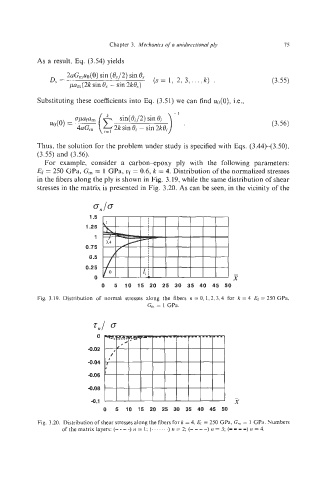
For example, consider a carbon-poxy ply with the following parameters:
Ef = 250 GPa, G, = 1 GPa, uf = 0.6, k = 4. Distribution of the normalized stresses
in the fibers along the ply is shown in Fig. 3.19, while the same distribution of shear
stresses in the matrix is presented in Fig. 3.20. As can be seen, in the vicinity of the
0
1.5
1.25
1
0.75
0.5
0.25
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Fig. 3.19. Distribution of normal stresses along the fibers n = 0,1,2,3,4 for k = 4 Er = 250 GPa.
G, = 1 GPa.
0
-0.02
-0.04
4.06
4.08
-0.1
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Fig. 3.20. Distribution of shear stresses along the fibers fork = 4, Ef = 250 GPa, G,,,= 1 GPa. Numbers
of the matrix layers: (- -- -) n = I; (. .. .. ..) n = 2; (- -- -) n = 3; (- -- -) n = 4.