Page 93 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 93
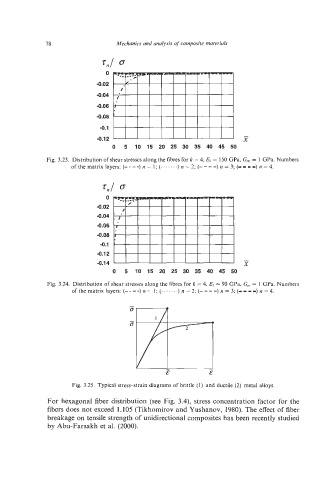
78 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
0
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
-0.08
-0.1
-
-0.12 I l l 1 I I I I I I I X
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Fig. 3.23. Distribution of shear stresses along the fibres fork = 4, EI.= 150 GPa, G,, = I GPa. Numbers
of the matrix layers: (- ---) n = I; (. . . . ...) n = 2; (- -- -) n = 3; (-I I9) n = 4.
Tnl 0
0
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
4.08
-0.1
-0.12
-
-0.14 X
o 5 io 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Fig. 3.24. Distribution of shear stresses along the fibrcs for k = 4, EI.= 90 GPa, G,,, = I GPa. Numbers
of the matrix layers: (- -- -) n = I; (. ... .. .) n = 2; (- -- -) n = 3; (- II9) n = 4.
Fig. 3.25. Typical stress-strain diagrams of brittle (1) and ductile (2) metal alloys.
For hexagonal fiber distribution (see Fig. 3.4), stress concentration factor for the
fibers does not exceed 1.105 (Tikhomirov and Yushanov, 1980). The effect of fiber
breakage on tensile strength of unidirectional composites has been recently studied
by Abu-Farsakh et al. (2000).