Page 31 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 31
18 Chapter 1
For relatively short beams, as already mentioned, the shearing effects are
important, and the shearing stresses are given by the equation:
where S is the shear force and the integral (the statical moment of area) is
taken for the area enclosed by an arbitrary line, parallel to the y-axis, situated
at a distance z measured from the cross-section center and one of the external
fibers. The shear strain is:
In this case, the total strain energy is:
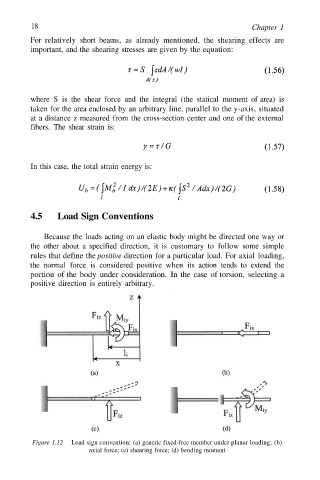
4.5 Load Sign Conventions
Because the loads acting on an elastic body might be directed one way or
the other about a specified direction, it is customary to follow some simple
rules that define the positive direction for a particular load. For axial loading,
the normal force is considered positive when its action tends to extend the
portion of the body under consideration. In the case of torsion, selecting a
positive direction is entirely arbitrary.
Figure 1.12 Load sign convention: (a) generic fixed-free member under planar loading; (b)
axial force; (c) shearing force; (d) bending moment