Page 279 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 279
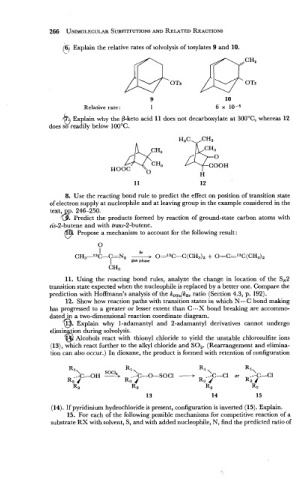
(6) Explain the relative rates of solvolysis of tosylates 9 and 10.
L'
9
Relative rate: 1
6 Explain why the weto acid 11 does not decarboxylate at 300°C, whereas 12
does so readily below 100°C.
8. Use the reacting bond rule to predict the effect on position of transition state
of electron supply at nucleophile and at leaving group in the example considered in the
p. 246-250.
. Predict the products formed by reaction of ground-state carbon atoms with
cis-2-butene and with trans-2-butene.
@l Propose a mechanism to account for the following result:
11 hv
CH3-'3C-C=N2 - O=13C=C(CH3)2 + 0=C=13C(CH3)2
I gap phase
CH3
11. Using the reacting bond rules, analyze the change in location of the SN2
transition state expected when the nucleophile is replaced by a better one. Compare the
prediction with Hoffmann's analysis of the k,,,/k,, ratio (Section 4.3, p. 192).
12. Show how reaction paths with transition states in which N.-C bond making
has progressed to a greater or lesser extent than C-.X bond breaking are accommo-
dated in a two-dimensional reaction coordinate diagram.
@. Explain why 1-adamantyl and 2-adamantyl derivatives cannot undergo
elimin tion during solvolysis.
6 Alcohols react with thionyl chloride to yield the unstable chlorosulfite ions
(13), which react further to the alkyl chloride and SO,. (Rearrangement and elimina-
tion can also occur.) In dioxane, the product is formed with retention of configuration
(14). If pyridinium hydrochloride is present, configuration is inverted (15). Explain.
15. For each of the following possible mechanisms for competitive reaction of a
substrate RX with solvent, S, and with added nucleophile, N, find the predicted ratio of