Page 67 - Mechatronic Systems Modelling and Simulation with HDLs
P. 67
56 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF MIXED SYSTEMS
R 1 = 10 R 2 = 100
~ AC = 220
C 1 = 0.01 L 1 = 0.1
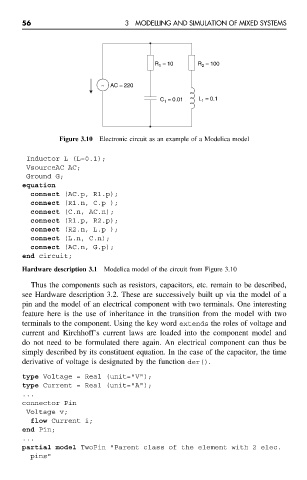
Figure 3.10 Electronic circuit as an example of a Modelica model
Inductor L (L=0.1);
VsourceAC AC;
Ground G;
equation
connect (AC.p, R1.p);
connect (R1.n, C.p );
connect (C.n, AC.n);
connect (R1.p, R2.p);
connect (R2.n, L.p );
connect (L.n, C.n);
connect (AC.n, G.p);
end circuit;
Hardware description 3.1 Modelica model of the circuit from Figure 3.10
Thus the components such as resistors, capacitors, etc. remain to be described,
see Hardware description 3.2. These are successively built up via the model of a
pin and the model of an electrical component with two terminals. One interesting
feature here is the use of inheritance in the transition from the model with two
terminals to the component. Using the key word extends the roles of voltage and
current and Kirchhoff’s current laws are loaded into the component model and
do not need to be formulated there again. An electrical component can thus be
simply described by its constituent equation. In the case of the capacitor, the time
derivative of voltage is designated by the function der().
type Voltage = Real (unit="V");
type Current = Real (unit="A");
...
connector Pin
Voltage v;
flow Current i;
end Pin;
...
partial model TwoPin "Parent class of the element with 2 elec.
pins"