Page 122 - Mechatronics for Safety, Security and Dependability in a New Era
P. 122
Ch22-I044963.fm Page 106 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 3:32 PM
Ch22-I044963.fm
106
106 Page 106 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 3:32 PM
b) Relational design information
For the case of geometric type change, the system should handle the capability to maintain the
members of groups. Where, relational design information consists of two groups in Fig. l-(2).
If parallelism is defined between two initial lines, the system should add the axis of the rotated
object as a group member when the rotated object is generated.
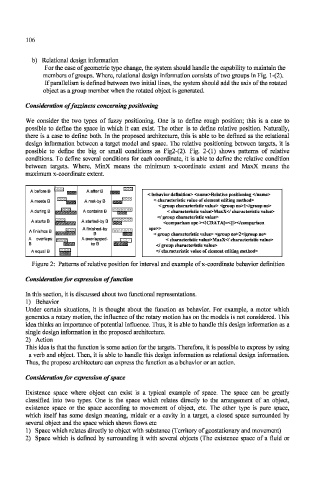
Consideration of fuzziness concerning positioning
We consider the two types of fuzzy positioning. One is to define rough position; this is a case to
possible to define the space in which it can exist. The other is to define relative position. Naturally,
there is a case to define both. In the proposed architecture, this is able to be defined as the relational
design information between a target model and space. The relative positioning between targets, it is
possible to define the big or small conditions as Fig2-(2). Fig. 2-(l) shows patterns of relative
conditions. To define several conditions for each coordinate, it is able to define the relative condition
between targets. Where, MinX means the minimum x-coordinate extent and MaxX means the
maximum x-coordinate extent.
< behavior definition> <name>Relative positioning </name>
< characteristic value of element editing method>
< group characteristic valuc> <group no>l </group no>
< characteristic value>MaxX</ characteristic value>
</ group characteristic value>
<comparison ope ><!CDATA|=<||x/comparison
ope»
< group characteristic value> <group no>2</group no>
< characteristic value>MaxX</ characteristic value>
</ group characteristic value>
</ characteristic value of element editing method>
Figure 2: Patterns of relative position for interval and example of x-coordinate behavior definition
Consideration for expression of function
In this section, it is discussed about two functional representations.
1) Behavior
Under certain situations, it is thought about the function as behavior. For example, a motor which
generates a rotary motion, the influence of the rotary motion has on the models is not considered. This
idea thinks an importance of potential influence. Thus, it is able to handle this design information as a
single design information in the proposed architecture.
2) Action
This idea is that the function is some action for the targets. Therefore, it is possible to express by using
a verb and object. Then, it is able to handle this design information as relational design information.
Thus, the propose architecture can express the function as a behavior or an action.
Consideration for expression of space
Existence space where object can exist is a typical example of space. The space can be greatly
classified into two types. One is the space which relates directly to the arrangement of an object,
existence space or the space according to movement of object, etc. The other type is pure space,
which itself has some design meaning, midair or a cavity in a target, a closed space surrounded by
several object and the space which shows flows etc
1) Space which relates directly to object with substance (Territory of geostationary and movement)
2) Space which is defined by surrounding it with several objects (The existence space of a fluid or