Page 403 - Mechatronics for Safety, Security and Dependability in a New Era
P. 403
Ch78-I044963.fm Page 387 Monday, August 7, 2006 11:30 AM
Page 387
Monday, August 7,2006
Ch78-I044963.fm
11:30 AM
387
387
LEARNING FOR HAND REACHING PROBLEM OF TWO-LINK MANIPULATOR
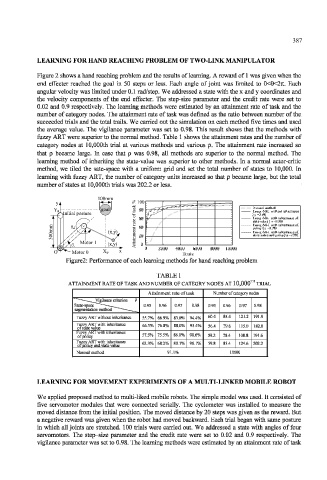
Figure 2 shows a hand reaching problem and the results of learning. A reward of 1 was given when the
end effecter reached the goal in 50 steps or less. Each angle of joint was limited to 0<6<2TI. Each
angular velocity was limited under 0.1 rad/step. We addressed a state with the x and y coordinates and
the velocity components of the end effecter. The step-size parameter and the credit rate were set to
0.02 and 0.9 respectively. The learning methods were estimated by an attainment rate of task and the
number of category nodes. The attainment rate of task was defined as the ratio between number of the
succeeded trials and the total trails. We carried out the simulation on each method five times and used
the average value. The vigilance parameter was set to 0.98. This result shows that the methods with
fuzzy ART were superior to the normal method. Table 1 shows the attainment rates and the number of
category nodes at 10,000th trial at various methods and various p. The attainment rate increased so
that p became large, hi case that p was 0.98, all methods are superior to the normal method. The
learning method of inheriting the state-value was superior to other methods. In a normal actor-critic
method, we tiled the sate-space with a uniform grid and set the total number of states to 10,000. In
learning with fuzzy ART, the number of category units increased so that p became large, but the total
number of states at 10,000th trials was 202.2 or less.
100mm
. Normal method
1'uzzy ARI without inheritam
(,« =0.98)
stato"valuc O =0.98)
Fuzzy ART with inheritance of
policy (p =0.98)
FuzzvART willi inheritance of
state-Value and policy! ,0-0.98)
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000
- Motor 0 X g Trials
Figure2: Performance of each learning methods for hand reaching problem
TABLE 1
ATTAINMENT RATE OF TASK AND NUMBER OF CATEGRY NODES AT 10,000™ TRIAL
Attainment rate of task Number of category nodes
—-^^Vigilance criterion P
State-space^^^^^^^^ 0.95 0.96 0.97 0.98 0.95 0.96 0.97 0.98
segmentation method ^ ^ - ^ ^ ^
Fuzzy ART without inheritance 55.7% 66.9% 83.0% 94.4% 60.4 85.4 121.2 191.0
Fuzzy ART with inheritance 66.5% 76.8% 88.0% 95.4% 56.4 79.6 182.8
ol'state value 115.0
Fuzzy ARF with inheritance
ofpolicv 57.5% 75.5% 86.0% 90.6% 59.2 78.4 108.8 191.6
Fuzzy ART with inheritance 62.3% 68.2% 80.1% 90.1% 59.8 85.4 124.6 202.2
ofpolicv and state value
Normal method 91.1% 10000
LEARNING FOR MOVEMENT EXPERIMENTS OF A MULTI-LINKED MOBILE ROBOT
We applied proposed method to multi-liked mobile robots. The simple model was used. It consisted of
five servomotor modules that were connected serially. The cyclometer was installed to measure the
moved distance from the initial position. The moved distance by 20 steps was given as the reward. But
a negative reward was given when the robot had moved backward. Each trial began with same posture
in which all joints are stretched. 100 trials were carried out. We addressed a state with angles of four
servomotors. The step-size parameter and the credit rate were set to 0.02 and 0.9 respectively. The
vigilance parameter was set to 0.98. The learning methods were estimated by an attainment rate of task