Page 118 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 118
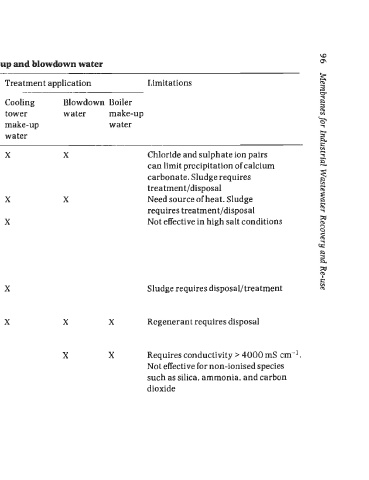
Table 3.5 Treatment options for controlling salts and nutrients in make-up and blowdown water
Treatment goal(s) Treatment approach Description Treatment application Limitations
Cooling Blowdown Boiler
tower water make-up
make-up water
water
Reduce scale-forming Lime softening Use of lime to precipitate cations, X X Chloride and sulphate ion pairs
potential, remove metals, and phosphorus from can limit precipitation of calcium
phosphorus, increase pH solution carbonate. Sludge requires
treatment/disposal
Hot process Use of lime and soda ash under X X Need source of heat. Sludge
softening elevated temperature conditions requires treatment/disposal
Removal/conversion of Biological nutrient Combination of aerobic. anoxic, X Not effective in high salt conditions
nitrogen; removal of removal and anaerobic processes to
phosphorus optimise conversion of organic
and ammonia nitrogen to
molecular nitrogen (N2) and
removal of phosphorus
Coagulation and Use of aluminium or iron salts to X Sludge requires disposal/treatment
precipitation promote precipitation of
phosphorus
Removal of calcium, Ion exchange Exchange of ions between an X X X Regenerant requires disposal
magnesium, iron, exchange resin and water using
ammonium, nitrate, a flow-through reactor
and other dissolved ions Electrodialysis Membrane-based process using X X Requires conductivity > 4000 mS cm-'.
reversal an electric fleld to separate ionic Not effective for non-ionised species
(Section 2.4.2) constituents across alternating such as silica, ammonia, and carbon
anion-selective and cation- dioxide
semi-permeable membranes