Page 146 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 146
120 Membranesfor Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-use
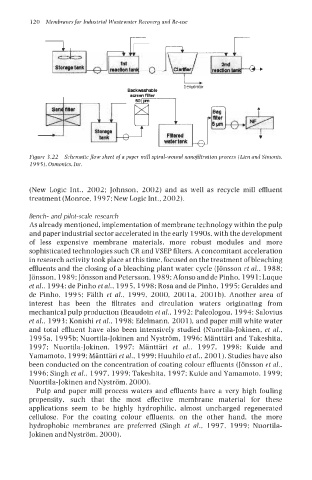
Dehydrator
Backnsshable
1
San mer
~
Filtered
water lank
Figure 3.22 Schematic flow sheet of a paper mill spiral-wound nunofiltration process (Lien and Simonis.
1995), Osmonics, Inc.
(New Logic Int., 2002; Johnson, 2002) and as well as recycle mill effluent
treatment (Monroe, 1997; New LogicInt., 2002).
Bench- and pilot-scale research
As already mentioned, implementation of membrane technology within the pulp
and paper industrial sector accelerated in the early 1990s, with the development
of less expensive membrane materials, more robust modules and more
sophisticated technologies such CR and VSEP filters. A concomitant acceleration
in research activity took place at this time, focused on the treatment of bleaching
effluents and the closing of a bleaching plant water cycle (Jonsson et al., 1988;
Jonsson, 19 8 9; Jonsson and Petersson, 19 8 9; Afonso and de Pinho, 19 9 1 ; Luque
et al., 1994; de Pinho et al., 1995, 1998; Rosa and de Pinho, 1995; Geraldes and
de Pinho, 1995; Falth et al., 1999, 2000, 2001a, 2001b). Another area of
interest has been the filtrates and circulation waters originating from
mechanical pulp production (Beaudoin et al., 1992; Paleologou, 1994; Salovius
et al., 1993; Konishi et al., 1998; Edelmann, 2001). and paper mill white water
and total effluent have also been intensively studied (Nuortila-Jokinen, et al.,
1995a, 1995b; Nuortila-Jokinen and Nystrom, 1996; Manttari and Takeshita,
1997; Nuortila-Jokinen, 1997; Manttari et al., 1997, 1998; Kuide and
Yamamoto, 1999; Manttari et al., 1999; Huuhilo et al., 2001). Studies have also
been conducted on the concentration of coating colour effluents (Jonsson et al.,
1996; Singh et al., 1997, 1999; Takeshita, 1997; Kuide and Yamamoto, 1999;
Nuortila-Jokinen and Nystrom, 2000).
Pulp and paper mill process waters and effluents have a very high fouling
propensity, such that the most effective membrane material for these
applications seem to be highly hydrophilic, almost uncharged regenerated
cellulose. For the coating colour effluents, on the other hand, the more
hydrophobic membranes are preferred (Singh et aZ., 1997, 1999; Nuortila-
Jokinen and Nystrom, 2000).